- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Use of erbium lasers safe and effective for removal of ceramic restorations, may not harm abutment or prosthesis
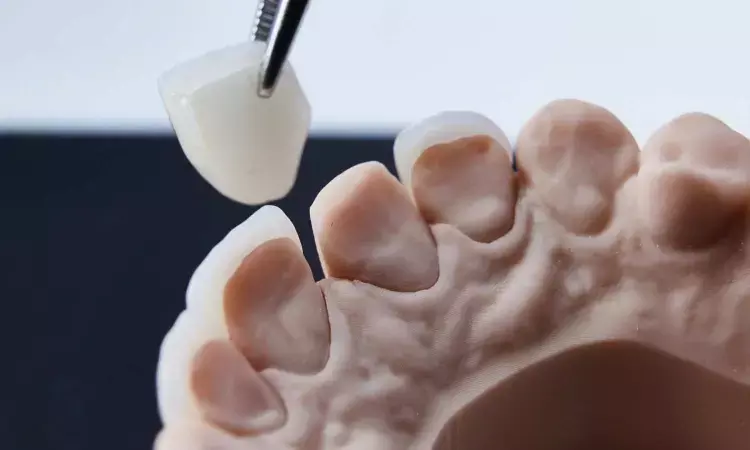
A recent study delved into the efficacy and practicality of employing Erbium lasers for the removal of ceramic restorations and appliances from natural teeth and dental implant abutments in clinical practice. This study was published in Plos One journal by Janina G. and colleagues.
This innovative approach aimed to assess the success rates, time efficiency, and safety of using Er,Cr:YSGG and Er:YAG lasers in diverse clinical scenarios. A retrospective analysis encompassing 29 clinical cases with a total of 52 abutments was conducted. Various factors, including prosthetic type and material, cement type, laser settings, retrieval time, and success, were meticulously evaluated.
The key findings of the study were:
Over 95% success was achieved, with 50 out of 52 abutments successfully retrieved using Er,Cr:YSGG (N = 6) or Er:YAG (N = 46) lasers.
The study included 13 lithium disilicate and 39 zirconia units, comprising veneers, single crowns, and fixed partial dentures (FPDs).
Varying retrieval times were noted based on the restoration type, material thickness, cement type, and retention form/fitting. For instance, veneers took 2.25 ±0.61 minutes, crowns 6.89 ±8.07 minutes, and FPDs 25 ±10 minutes per abutment.
Debonding time was influenced by laser settings, materials, and prosthesis types.
The study's findings endorse Erbium lasers as a safe and effective alternative to invasive methods for removing ceramic restorations. Notably, these lasers allowed for successful debonding without causing harm to the abutment or prosthesis. Laser-assisted debonding showcased its potential by enabling recementation of restorations during the same appointment, presenting a conservative and practical option for ceramic crown retrieval in clinical settings.
Reference:
Deeb, J. G., Grzech-Lesniak, K., & Bencharit, S. Evaluation of the effectiveness and practicality of erbium lasers for ceramic restoration removal: A retrospective clinical analysis. PloS One,2023;18(12):e0295957. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0295957
Dr Riya Dave has completed dentistry from Gujarat University in 2022. She is a dentist and accomplished medical and scientific writer known for her commitment to bridging the gap between clinical expertise and accessible healthcare information. She has been actively involved in writing blogs related to health and wellness.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


