- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Rare case of Rosai-Dorfman disease in woman with cervical cancer and syphilis: A report
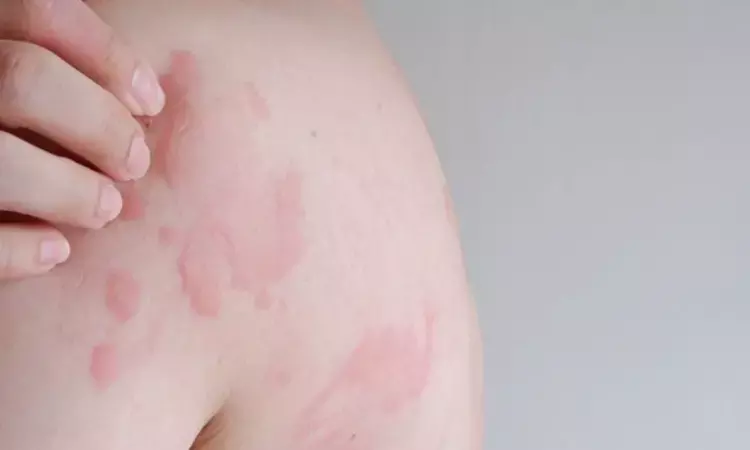
Poland: A recent case report and a review of literature published in BMC Dermatology have described the presence of cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease (CRDD) in a patient with late syphilis and cervical cancer.
Cutaneous Rosai – Dorfman disease is a benign, rare condition which is difficult to diagnose due to an absence of general symptoms and lymphadenopathy. It is an extremely rare variant of an idiopathic histiocytic proliferative disorder, which may manifest as non-specific papules, macules, nodules or plaques ranging in size and colour from red-brown to yellow–red. Histopathologic examination with immunohistochemical staining exhibiting characteristic and reproducible findings is critical for an accurate diagnosis.
In the presented case, activated histiocytes shown in a lesional skin might be a response to immune dysregulation related to untreated, chronic STIs (sexually transmitted infections) and cancer.
The case in question is of a 52-year-old female presented with three reddish-brown, gradually enlarging nodules on the right upper extremity lasting six months. The patient denied weight loss, fever, and malaise.
"To the best of our knowledge, it is the first case of CRDD reported internationally from Poland and co-existing with STIs and cervical cancer," Angelika Bielach – Bazyluk from the Medical University of Bialystok, Białystok in Poland, and colleagues wrote.
Imaging tests and clinical examination revealed no sign of lymphadenopathy. A biopsy specimen of a nodule revealed a dense dermal polymorphic infiltrate with numerous histiocytes showing emperipolesis phenomenon. Histiocytes' immunohistochemical staining showed CD68 and S-100 protein but without CD1a.
The findings were consistent with the characteristics of Cutaneous Rosai – Dorfman disease. Additionally, a routine serological screening and confirmatory serological tests for syphilis were positive. A diagnosis of syphilis of unknown duration was made. There was an increase in the IgG antibodies titre against Chlamydia trachomatis. An isolated sensory impairment over the right trigeminal nerve was revealed in neurological consultation.
Because of the patient's bleeding complaints after sexual intercourse, a comprehensive gynaecological assessment led to a cervical cancer diagnosis. After three months, the initial methotrexate therapy was discontinued due to neutropenia. Complete surgical excision was recommended, as further therapy with dapson was ineffective.
Due to the outbreak of coronavirus disease (COVID-19), the procedure has not been carried out so far. The patient's husband also had positive syphilis serology and was given doxycycline treatment. Both completed appropriate after-treatment follow-ups.
The authors highlighted the importance of consideration of rare entities in the differential diagnosis of non-specific skin lesions, particularly since the proper one could be made only based on techniques such as immunohistochemistry. Based on the examination performed, the authors assumed that they reported a case of purely CRDD in a woman with complex medical history involving several STIs, malignancy, and unexplained neurologic symptoms.
According to the authors, the report initially seemed to support the hypothesis that CRDD may be a response to immune dysregulation related to co-existing STIs and neoplastic processes in this specific case.
"It could be expected that skin lesions will resolve after treating the infections and hysterectomy," the authors explained. "However, the patient failed to respond to the treatment, rendering the hypothesis questionable. CRDD with limited lesions may benefit more from the surgical intervention than pharmacotherapy."
Reference:
Bielach – Bazyluk, A., Serwin, A.B., Pilaszewicz – Puza, A. et al. Cutaneous Rosai – Dorfman disease in a patient with late syphilis and cervical cancer – case report and a review of literature. BMC Dermatol 20, 19 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12895-020-00115-w
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


