- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Management of atopic dermatitis with topical therapies in adults: Updated guideline by AAD
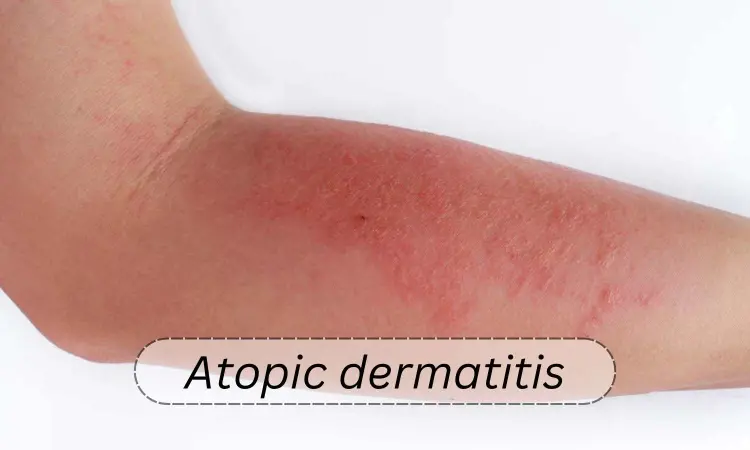
USA: A recent article published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology reports updated guidelines of care for managing atopic dermatitis in adults with topical therapies.
This update reflects the latest advances in topical medications available to help adults with atopic dermatitis.
Atopic dermatitis also called eczema or atopic eczema, is a common skin condition that affects 1 in 10 Americans. Atopic dermatitis occurs most commonly in children; it also affects adults and can significantly impact the patient's quality of life. The guideline, which is an update to the 2014 recommendations for AD management with topics therapies, outlines best practices for topical treatment of the disease and is developed by an expert workgroup of 12 physicians, including 11 dermatologists, an allergist/pediatrician and one patient representative.
The workgroup developed 11 recommendations on the management of AD in adults with topical therapies, including non-prescription agents and prescription topical corticosteroids (TCSs), phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors (PDE-4), antimicrobials, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, calcineurin inhibitors (TCIs), and antimicrobials.
Strong recommendations are made for using moisturizers, TCSs, TCIs, topical PDE-4 and JAK inhibitors. Conditional recommendations are made for the use of bathing and wet wrap therapy and against the use of topical antimicrobials, antihistamines, and antiseptics.
Strong recommendations were made for the use of the following:
· Topical calcineurin inhibitors (pimecrolimus 1% cream and tacrolimus 0.03% or 0.1% ointment) reduce patients' inflammation and itching and decrease their flare-ups.
· Moisturizers help to relieve patients' dry, cracked skin, decrease inflammation, and reduce the severity of and increase the time between flare-ups.
· Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor (crisaborole ointment) can reduce patients' inflammation, help relieve itching, and decrease infections.
· Topical corticosteroids are commonly used as the first-line treatment for patients with atopic dermatitis in all skin regions. They help to relieve itching, decrease inflammation and can decrease infections.
· Janus kinase inhibitor (ruxolitinib cream) can be used short term to ease the inflammation and itching of patients with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis.
· The guidelines provide conditional recommendations for bathing and wet wrap therapy. Conditional recommendations apply to most patients, but the most appropriate action may differ depending on individual patient factors.
· Bathing, followed by moisturization, helps patients hydrate the skin. Bleach baths can help patients prevent infection and eliminate bacteria on their skin.
· Wet wrap therapy utilizes wet bandages to help hydrate and soothe patients' skin. This treatment provides a barrier against scratching, helps to decrease redness and inflammation, and can reduce the bacteria on patients' skin.
Reference:
"Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis in adults with topical therapies," was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2022.12.029
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


