- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Antioxidants added to medical devices may cause allergic contact dermatitis
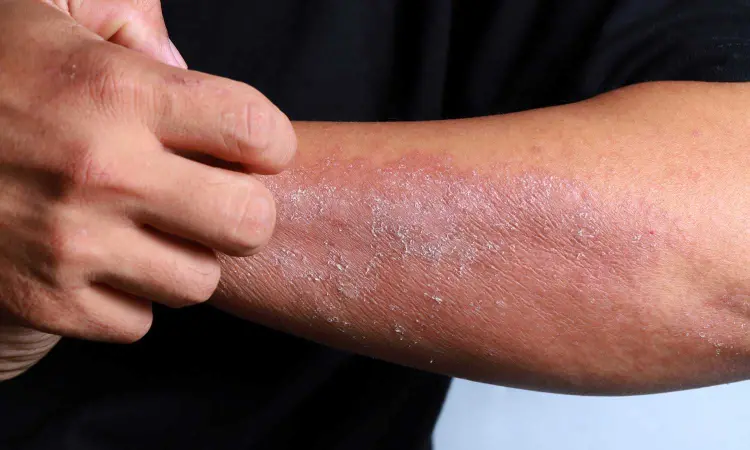
Sweden: A recent study has revealed that antioxidants, added to medical devices to protect polymers or adhesives, may also lead to allergic reactions in some individuals. The study was published in Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine Cutaneous Dermatitis on 16 May 2023.
"The antioxidant 4,4′-thiobis(2-tert-butyl-5-methylphenol) may cause allergic contact dermatitis after exposure to different medical devices," the researchers wrote in their study.
The study aimed to provide data on sensitization to 4,4′-thiobis(2-tert-butyl-5-methylphenol), an antioxidant commonly found in certain types of medical devices. Researchers Annarita Antelmi and team conducted patch testing with 1% pet of 4,4′-thiobis(2-tert-butyl-5-methylphenol). They used gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to identify the presence of the antioxidant in various medical device products.
The case series presented data from six patients who developed eczematous reactions after using various types of medical devices. All of these patients demonstrated positive reactions to 4,4′-thiobis(2-tert-butyl-5-methylphenol), and at least one product containing this antioxidant. Moreover, the concentrations of the antioxidant varied across different products, as determined by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis.
The presence of 4,4′-thiobis(2-tert-butyl-5-methylphenol) has been identified in various medical devices, including wound dressings and surgical tape. These findings highlight the need for increased awareness among healthcare professionals and patients regarding the potential allergenic properties of antioxidants used in medical devices. It is crucial to consider the possibility of allergic reactions when selecting and using such devices, especially in patients with a history of dermatological sensitivities.
The findings revealed that six patients who experienced eczematous reactions to different medical devices also exhibited contact allergy to 4,4′-thiobis(2-tert-butyl-5-methylphenol). Further analysis using GC-MS confirmed the presence of this antioxidant in the products.
The implications of this research suggest that the antioxidant 4,4′-thiobis(2-tert-butyl-5-methylphenol) can cause allergic contact dermatitis when individuals are exposed to different medical devices. Further research and validation are necessary to fully understand the scope and mechanisms of antioxidant-induced contact dermatitis in medical devices. This information will facilitate the development of preventive measures and alternative materials that minimize the risk of allergic reactions while maintaining the functionality and efficacy of medical devices.
Healthcare providers should stay informed about the latest research in this area and consider patch testing for patients who experience unexplained dermatological reactions after using medical devices. By identifying and addressing the underlying causes of contact dermatitis, healthcare professionals can ensure optimal patient care and prevent potential complications associated with allergic reactions to medical devices.
Reference:
Antelmi, A., Lejding, T., Bruze, M., Mowitz, M., & Dahlin, J. (2023). 4,4’-Thiobis(2-tert-butyl-5-methylphenol), an antioxidant in medical devices that may cause allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. https://doi.org/10.1111/cod.14335.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


