- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Bimekizumab scores over adalimumab in achieving plaque psoriasis clearance: NEJM
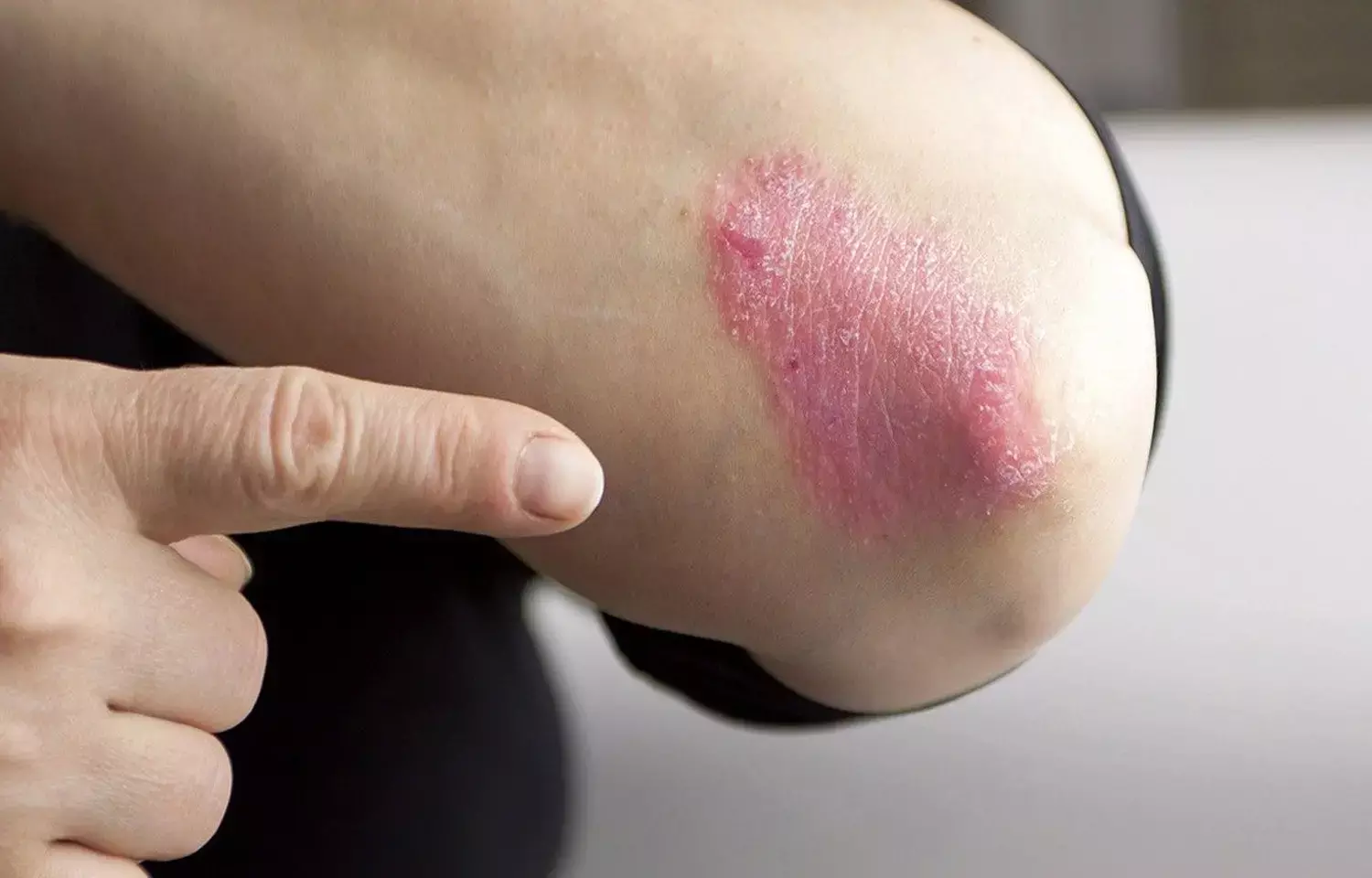
UK: Bimekizumab was shown to be noninferior and superior to adalimumab in reducing signs and symptoms of plaque psoriasis in a 56-week trial. However, bimekizumab was associated with a higher frequency of diarrhea and oral candidiasis.
The findings of the study were reported at the American College of Dermatology virtual meeting 2021 and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Bimekizumab, a monoclonal IgG1 antibody, selectively inhibits interleukin-17A and interleukin-17F. The safety and efficacy of bimekizumab as compared with the tumor necrosis factor inhibitor adalimumab has not been extensively examined in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Richard B. Warren, University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom, and colleagues conducted this study to determine the same.
478 patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis were randomly assigned in a ratio of 1:1:1 to receive subcutaneous bimekizumab at a dose of 320 mg every 4 weeks for 56 weeks (n=158); bimekizumab at a dose of 320 mg every 4 weeks for 16 weeks, then every 8 weeks for weeks 16 to 56 (n=161); or subcutaneous adalimumab at a dose of 40 mg every 2 weeks for 24 weeks, followed by bimekizumab at a dose of 320 mg every 4 weeks to week 56 (n=159).
The primary end points were a 90% or greater reduction from baseline in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score (PASI 90 response; PASI scores range from 0 to 72, with higher scores indicating worse disease) and an Investigator's Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1, signifying clear or almost clear skin (scores range from 0 [clear skin] to 4 [severe disease]), at week 16.
Key findings of the study include:
- At week 16, a total of 275 of 319 patients (86.2%) who received bimekizumab (both dose groups combined) and 75 of 159 (47.2%) who received adalimumab had a PASI 90 response (adjusted risk difference, 39.3 percentage points).
- A total of 272 of 319 patients (85.3%) who received bimekizumab and 91 of 159 (57.2%) who received adalimumab had an IGA score of 0 or 1 (adjusted risk difference, 28.2 percentage points).
- The most common adverse events with bimekizumab were upper respiratory tract infections, oral candidiasis (predominantly mild or moderate as recorded by the investigator), hypertension, and diarrhea.
"In this 56-week trial, bimekizumab was noninferior and superior to adalimumab through 16 weeks in reducing symptoms and signs of plaque psoriasis but was associated with a higher frequency of oral candidiasis and diarrhea," concluded the authors. "Longer and larger trials are required to determine the efficacy and safety of bimekizumab as compared with other agents in the treatment of plaque psoriasis."
Reference:
The study titled, "Bimekizumab versus Adalimumab in Plaque Psoriasis," is published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
DOI: https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2102388
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


