- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Experimental topical PDE4 inhibitor showed superior efficacy for atopic dermatitis, plaque psoriasis: JAMA
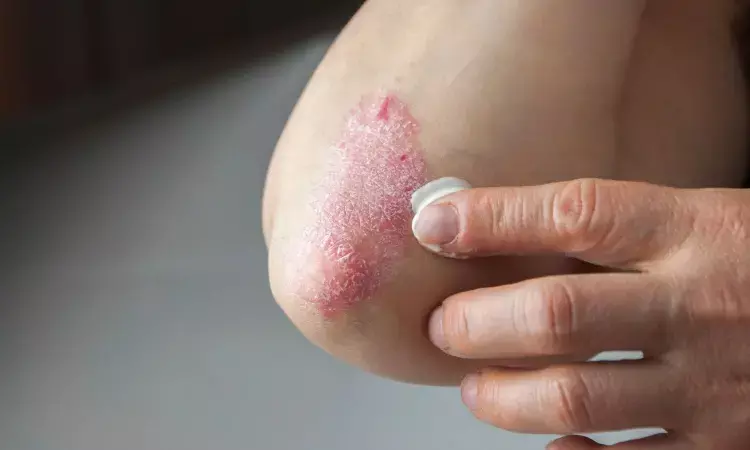
USA: A phase 2a study published in JAMA Dermatology revealed the superior efficacy of an experimental topical phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor to a vehicle in patients with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis (AD) and plaque psoriasis.
The phase 2a randomized clinical trial of 104 patients comprising 70 patients with AD and 34 with plaque psoriasis revealed that once-daily administration of 0.01% PF-07038124 was more effective than vehicle after six weeks of treatment. PF-07038124 was generally well tolerated, with no application site reactions.
Plaque psoriasis and atopic dermatitis are inflammatory, chronic skin diseases associated with a substantial socioeconomic and health-related burden. Topical treatments, such as corticosteroids and daily emollients, are first-line therapies for mild to moderate AD and plaque psoriasis. However, corticosteroids are linked with systemic adverse events (AEs) and application site reactions, such as stinging and burning. Therefore, there is a need for new treatments for plaque psoriasis and AD with robust efficacy and fewer adverse reactions.
Topical PF-07038124 is designed to be a potent, oxaborole-based PDE4 inhibitor with immunomodulatory activity in T-cell–based assays, leading to the inhibition of IL-13 and IL-4; thus, it could provide therapeutic benefit in the treatment of plaque psoriasis and AD. Lawrence F. Eichenfield, Department of Dermatology, University of California, San Diego, School of Medicine, and colleagues aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of the topical PDE4 inhibitor PF-07038124 in patients with AD and plaque psoriasis.
For this purpose, the researchers conducted a phase 2a, randomized, double-blind clinical trial from 2020 to 2021, at 34 sites across four countries. Eligible patients (aged 18-70 years) had plaque psoriasis (covering 5%-15% of body surface area) or mild to moderate AD (covering 5%-20% of body surface area).
104 patients (mean age 43.0 years, 52.9% were women) were randomized in the ratio of 1:1 to PF-07038124, 0.01%, topical ointment or vehicle once daily for six weeks.
The study's primary endpoint was the per cent change from baseline (CFB) in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) total score among AD patients and in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score among plaque psoriasis patients at week 6. Safety measures included treatment-emergent adverse events, including application site reactions.
Based on the study, the researchers reported the following findings:
- 104 patients were randomized, including 70 with AD (58.6% women; mean ages, 41.4 years in the PF-07038124 group and 36.1 years in the vehicle group) and 34 with plaque psoriasis (58.8% men; mean ages, 51.8 years in the PF-07038124 group and 51.2 years in the vehicle group). Baseline characteristics were generally balanced.
- At week 6, the PF-07038124 groups showed significantly greater improvements compared with vehicle groups in EASI (least-squares mean CFB, −74.9% vs −35.5%; difference, −39.4%) and PASI scores (CFB, −4.8 vs 0.1; difference, −4.9).
- The number of patients with treatment-emergent adverse events was comparable between treatment groups in patients with AD (PF-07038124, 25.0%; vehicle, 26.5%) and plaque psoriasis (PF-07038124, 17.6%; vehicle, 35.3%).
- There were no application site reactions with PF-07038124 treatment.
In patients with mild to moderate AD and plaque psoriasis, PF-07038124 treatment demonstrated superior efficacy, compared with vehicle. The drug was well tolerated, with no treatment-related TEAEs or application site reactions reported in the PF-07038124 group.
"Long-term data should be collected in larger studies to confirm the persistence of the safety profile and efficacy of PF-07038124," the researchers concluded.
Reference:
Eichenfield LF, Tarabar S, Forman S, et al. Efficacy and Safety of PF-07038124 in Patients With Atopic Dermatitis and Plaque Psoriasis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Dermatol. Published online December 20, 2023. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2023.4990
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


