- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Exposure to cobalt may lead to allergic contact dermatitis in children: Study
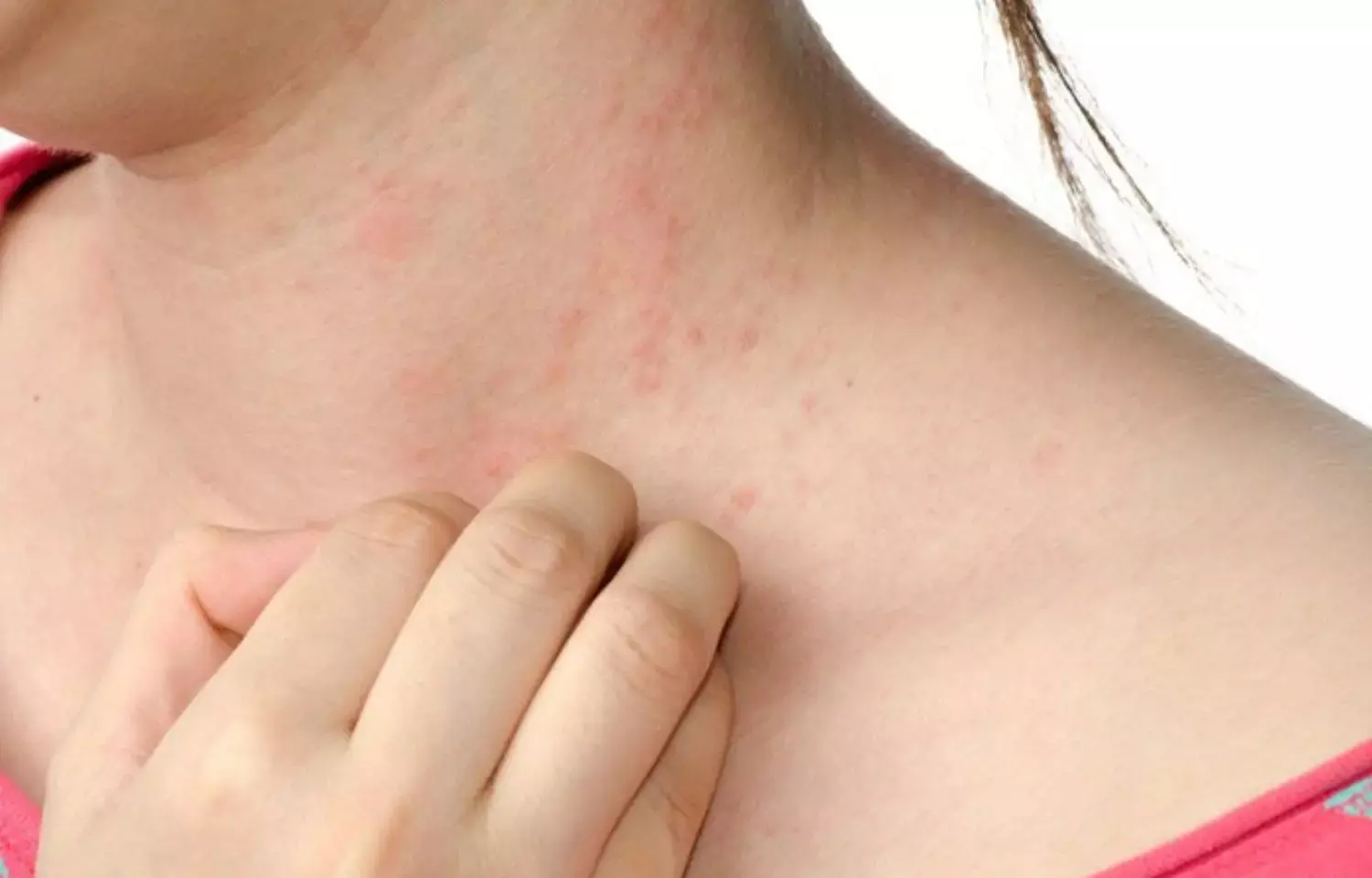
USA: A new study findings report that allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) reactions are common among children exposed to cobalt, with the most common site being the trunk, face, and ears. The article was published in Contact Dermatitis.
An allergic contact dermatitis is a form of dermatitis/eczema caused by an allergic reaction to a material, called an allergen, which comes in contact with the skin. Nickel, cobalt, and chromates are the most frequent allergens. Allergic contact dermatitis is also called contact allergy. Cobalt is known as a strong skin sensitizer. Cobalt allergy affects nearly 2% of the general population and can develop at any age, including in children. A patch test is a diagnostic method used identification of the etiologic agent of ACD.
Previous research has indicated that ACD to cobalt is more common in children and adolescents than in adults. , ACD is often underdiagnosed due to a lack of patch testing and misdiagnosis. To date, detailed information on sites and sources of cobalt ACD is limited.
Jonathan I. Silverberg, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, USA, and his team conducted a retrospective analysis study to assess trends in positive and clinically relevant patch test reactions to cobalt in children and associated patient characteristics, common sources, and body sites affected.
Researchers analyzed 1,919 children (<18 years) patch tested for cobalt by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group. They used cobalt in the forms of cobalt chloride 1% in petrolatum (pet.) and cobalt chloride hexahydrate 1.0% pet. It was left on site for 48 hours, and readings were taken at both 48 hours and 72-168 hours following placement. Researchers graded reactions on positive and negative scales which ranged from non-vesicular, indurated erythema and macular erythema or irritant. Allergen sources were classified in 228 options and 11 categories.
Key findings of the study,
• 228 (11.9%) and 127 (6.6%) had a positive/allergic or currently relevant patch test reaction to cobalt, respectively.
• The most common primary body sites affected were scattered generalized (30.0%), face, not otherwise specified (NOS, 10.6%), and trunk (10.1%).
• Patients with allergic and currently relevant allergic patch test reactions were more likely to have a primary site of the trunk and ears.
• Affected body site(s) varied by cobalt source among patients with currently relevant reactions, especially for less common sources
• The most commonly identified sources of cobalt included jewelry, belts, and clothing.
The authors conclude that in children positive patch test reactions to cobalt were very common. Most common body sites were scattered and generalized, including the trunk, face, and ears as the primary site. Also, the cobalt sources, varied by variation in the body site.
Reference:
Jonathan I. Silverberg,Nisha Patel,Erin M. Warshaw,Howard I. Maibach,Donald V. Belsito,Joel G. DeKoven,Kathryn A. Zug,James S. Taylor,Denis Sasseville,Vincent A. DeLeo et al. First published: 08 July 2022 https://doi.org/10.1111/cod.14185
BDS
Dr. Hiral patel (BDS) has completed BDS from Gujarat University, Baroda. She has worked in private dental steup for 8years and is currently a consulting general dentist in mumbai. She has recently completed her advanced PG diploma in clinical research and pharmacovigilance. She is passionate about writing and loves to read, analyses and write informative medical content for readers. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


