- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Hormonal IUDs Linked to Increased Risk of Rosacea in Women : Study
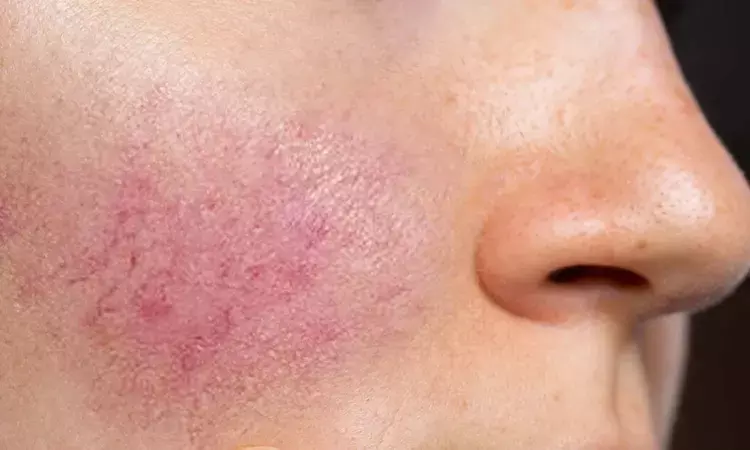
Researchers have found in a new study that Women using hormonal IUDs like Liletta and Mirena showed a higher likelihood of developing rosacea one year after insertion compared to those using nonhormonal copper IUDs.The increased risk was not observed with Skyla, a hormonal IUD that releases a lower dose of levonorgestrel.The study highlights a potential skin-related side effect associated with certain hormonal contraceptives.
Hormonal contraceptives manipulate estrogen and progesterone levels and have been associated with dermatologic side effects, including rosacea, a chronic skin condition marked by facial redness and inflammatory lesions.
This multicenter cohort study evaluated the incidence of rosacea among users of hormonal intrauterine devices (IUDs)-Liletta, Mirena, and Skyla-compared to nonhormonal copper IUD users. Women aged 18-50 who underwent IUD insertion and had a new diagnosis of rosacea (ICD-10-CM code L71) within 1, 3, or 5 years post-insertion were included. Those with prior rosacea or early IUD removal were excluded. Data were drawn from the TriNetX network. Incidence rates (IRs), incidence rate ratios (IRRs), and absolute risk differences (ARDs) were calculated, using the copper IUD group as the reference. Statistical significance (P ≤ .05) was determined via the Wald test. At 1-year postinsertion, Liletta users exhibited the highest IR of rosacea (634.28 per 100,000 person-years) with a significant IRR of 1.665 (P < .001).
Mirena users had an IR of 529.30 and an IRR of 1.389 (P < .001), while Skyla users had an IR of 409.00, but the IRR (1.074) was not significant (P = .696). At 3 years, Liletta maintained the highest IR (391.74) and a significant IRR of 1.751 (P < .001), followed by Mirena (IR 322.02, IRR 1.440, P < .001). Skyla's IRR remained non-significant. At 5 years, Liletta continued to show the highest IR (285.02) with an IRR of 1.788 (P < .001), and Mirena had an IR of 234.54 with a significant IRR of 1.472 (P < .001). Skyla's IRR remained statistically non-significant throughout all time points.
These findings suggest that Liletta and Mirena may be associated with an increased risk of developing rosacea compared to nonhormonal IUDs.
Reference:
Incidence of rosacea associated with hormonal intrauterine devices: A comparative study with nonhormonal intrauterine devices. Arza, Alexis et al. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Volume 92, Issue 2, 351 - 352
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


