- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
HPPF quick and effective way fy achieving hemostasis after punch biopsies: study
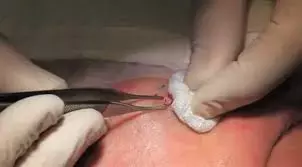
Hydrophilic polymer and potassium ferrate (HPPF) is a quick and effective way to achieve hemostasis after punch biopsies suggest a recent study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Skin biopsy is an important diagnostic procedure commonly performed in dermatology practice. Various methods of skin biopsy exist, and multiple factors are considered in choosing the most appropriate biopsy technique for a given situation. Among the most important factors are location and depth and breadth of sampling. An effort is made to provide the consulting pathologist with as much tissue as clinically reasonable, from a location with the highest chance of diagnostic yield, while causing as little disfigurement and compromise of function to the patient as possible. Biopsies can be categorized as incisional, in which only a portion of a lesion is sampled, or excisional in which the physician removes all of the visible lesion. An incisional biopsy can be performed as a shave, scissor, curettage, or punch specimen. Excisional biopsy is usually done with a full-thickness scalpel or a deeper oblique (shave or scoop) excision.
A punch biopsy is a procedure in which a small round piece of tissue about the size of a pencil eraser is removed using a sharp, hollow, circular instrument. The tissue is then checked under a microscope for signs of disease. A punch biopsy may be used to check for certain types of cancer, including skin, vulvar, and cervical cancer. It may also be used to check for certain skin conditions and changes that may lead to cancer.
Hydrophilic polymer and potassium ferrate (HPPF) is a hemostatic product sold as a powder in single-use tubes to achieve hemostasis. This retrospective chart review analyzed 73 cases among 46 hospitalized patients who had punch biopsies wherein Hydrophilic polymer and potassium ferrate was used for hemostasis. There were no complications such as prolonged pain, bleeding, infections, or concerns over scar appearance.
Thus, the study concluded that Hydrophilic polymer and potassium ferrate is a quick and effective way to achieve hemostasis after punch biopsies. It may be especially useful in patients with compromised hemostasis due to an underlying condition or medication.
Reference:
Victor Wu, et al. A Retrospective Analysis of Hydrophilic Polymer and Potassium Ferrate as a Well Tolerated Alternative to Suture for 4mm Punch Biopsies in Hospitalized Patients. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. August 05, 2022DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2022.08.007
Keywords:
HPPF, quick, effective, way, achieve, hemostasis, punch biopsies, Hydrophilic polymer and potassium ferrate, Victor Wu, Jaimie Lin, Jawaher Assed, Emily Altman, John R. Durkin, hydrophilic polymer, Woundseal, wound healing, potassium ferrate, biopsy
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


