- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Infection Risk among HS Patients Compared to Psoriasis: JAMA
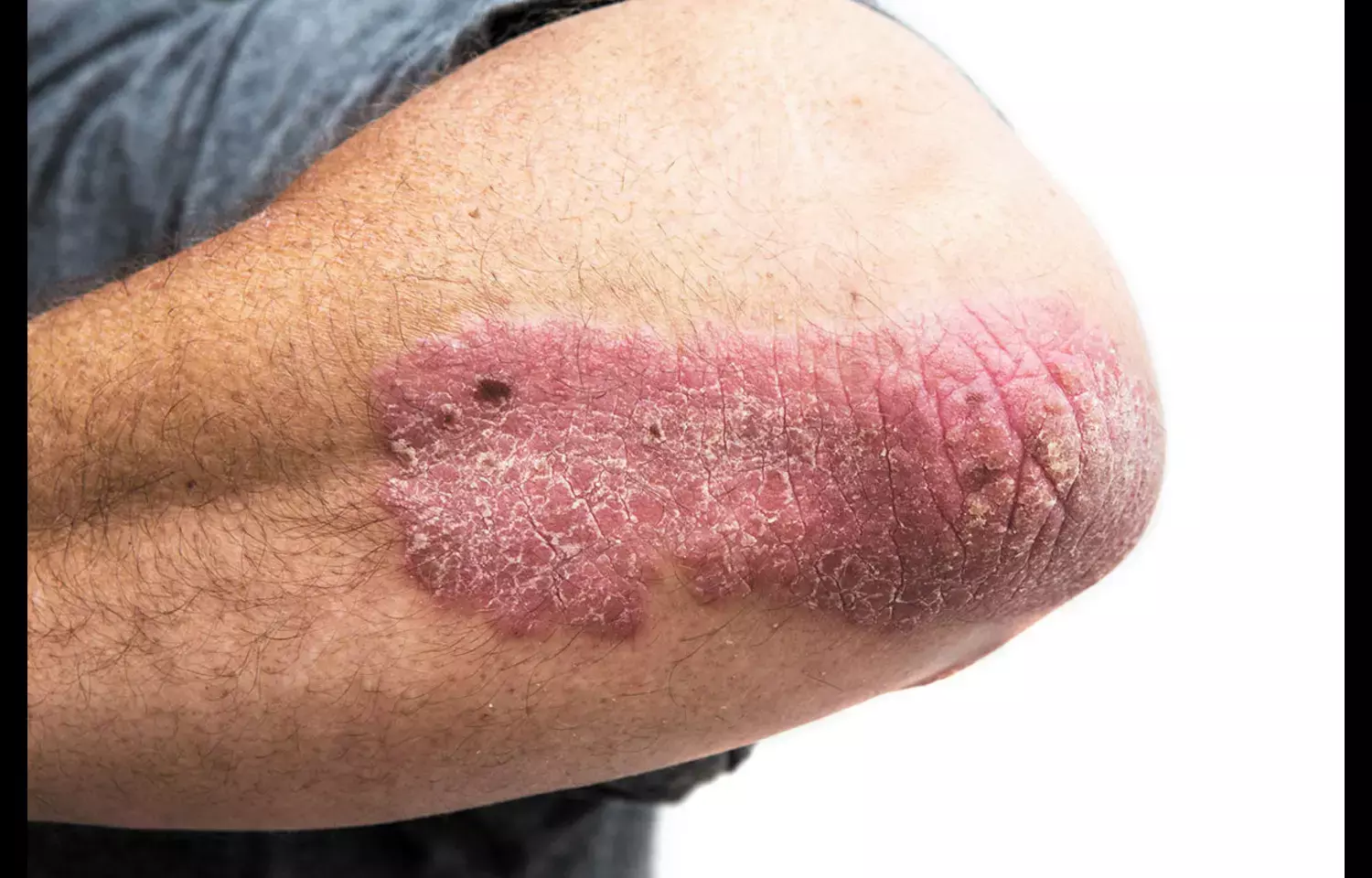
Adults with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) treated with adalimumab face a significantly higher risk of serious infections compared to those with psoriasis, according to a new cohort study published in JAMA Dermatology. Researchers analyzed U.S. insurance claims data of 10,349 adults initiating adalimumab between 2017–2020—1,650 with HS and 8,699 with psoriasis. They found that the HS group had a 53% higher hazard of hospitalization for noncutaneous infections (HR 1.53; 95% CI 1.34–1.86) after adjusting for confounders. Rates of sepsis (IRR 2.07; 95% CI 1.35–3.12) and genitourinary infections (IRR 2.22; 95% CI 1.22–3.86) were more than double in the HS cohort. HS patients also had a 28% higher odds of prolonged hospital stays (OR 1.28; 95% CI 1.13–1.45). Notably, HS patients were younger (mean age 36.2 vs. 46.5 years), more often female (77% vs. 50%), and had higher rates of obesity, Crohn’s disease, anxiety, and depression. The findings suggest that HS patients face a distinct infectious risk profile under immunosuppressive therapy compared to those with psoriasis. Researchers highlight the need for further studies to understand how disease severity, treatment regimens, and preventive strategies could mitigate this elevated infection risk. Until then, clinicians should remain vigilant when managing HS patients with adalimumab and consider close monitoring and tailored infection-prevention strategies.
Keywords: adalimumab, hidradenitis suppurativa, psoriasis, infection risk, serious infection, JAMA Dermatology, sepsis, genitourinary infection, hospitalization, cohort study
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.


