- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Isotretinoin Shows Promise for Acne in Transgender and Gender-Diverse Individuals on Masculinizing Hormone Therapy: JAMA
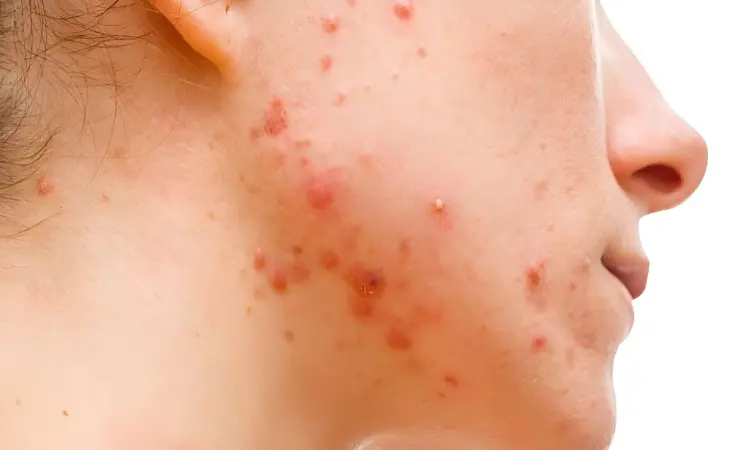
USA: In a groundbreaking study published in the JAMA Dermatology, researchers have shed light on the efficacy and safety of isotretinoin treatment for acne in transgender and gender-diverse individuals undergoing masculinizing hormone therapy. This research represents a significant step towards addressing a longstanding gap in dermatological care for this population.
The case series study of 55 transgender and gender-diverse individuals with acne who were receiving gender-affirming hormonal therapy revealed that treatment with isotretinoin was associated with clearance in 63.6% and improvement in 97.0% of patients treated with a cumulative dose of 120 mg/kg or more. However, premature treatment discontinuation was common and tied to poorer outcomes.
Acne is a common concern for individuals undergoing hormone therapy as part of their gender transition. Masculinizing hormone therapy, which typically involves the use of testosterone, can lead to an increase in sebum production, resulting in acne flare-ups. However, concerns about potential interactions between isotretinoin and hormone therapy have limited its use in this population.
While isotretinoin is a highly effective acne treatment, not much is known about its safety and effectiveness among transgender and gender-diverse individuals receiving gender-affirming hormonal therapy. James Choe, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, and colleagues aimed to evaluate clinical outcomes of isotretinoin among transgender and gender-diverse individuals receiving gender-affirming hormonal therapy.
For this purpose, the researchers conducted a multicenter retrospective case series study at four medical centers: the University of Pennsylvania, Mass General Brigham, Fenway Health, and Emory University. It included patients aged 12 to 49 years who were receiving masculinizing gender-affirming hormonal therapy and prescribed isotretinoin for the management of acne between 2015 and 2023.
The outcomes were the percentage of patients experiencing clearance or improvement of acne, and rates of acne recurrence. The researchers also evaluated adverse effects and reasons for treatment discontinuation.
The study led to the following findings:
- Among 55 included patients, the mean age was 25.4 years; 7.3% were Asian, 2 3.6% were Black, 7.2% were Hispanic, 1.8% multiracial, and 65.5% were White. The median isotretinoin course duration was 6 months, with a median cumulative dose of 132.7 mg/kg; the cumulative dose was less than 90 mg/kg for 29.1% of patients and less than 120 mg/kg for 40.0%.
- Isotretinoin was associated with improvement in 87.3% and clearance in 47.3% of patients.
- For the 33 patients treated with a cumulative dose of 120 mg/kg or more, these rates increased to 97.0% and 63.6% of patients, respectively.
- Among the 20 patients who achieved acne clearance and had any subsequent healthcare encounters, the risk of recurrence was 20.0%.
- The most frequently reported adverse effects were dryness (80.0%), joint pain (14.5%), and eczema (9.1%).
- Laboratory abnormalities were uncommon.
- Reasons for premature treatment discontinuation included cost, pharmacy issues, adverse effects, logistical reasons (scheduling), and wound healing concerns for gender-affirming surgery.
In the case series study of patients with acne who were receiving masculinizing gender-affirming hormonal therapy and underwent isotretinoin treatment, isotretinoin was often effective and well tolerated. However, premature treatment discontinuation was common and tied to poorer outcomes.
"There is a need for further efforts to understand optimal dosing and treatment barriers to improve outcomes in transgender and gender-diverse individuals receiving masculinizing gender-affirming hormonal therapy," the researchers concluded.
Reference:
Choe J, Shields A, Ferreira A, et al. Isotretinoin for Acne in Transgender and Gender-Diverse Individuals Receiving Masculinizing Hormone Therapy. JAMA Dermatol. Published online May 29, 2024. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2024.1420
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


