- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Low-Dosage oral isotretinoin safe and Efficacious in Patients with Acne, reaffirms study
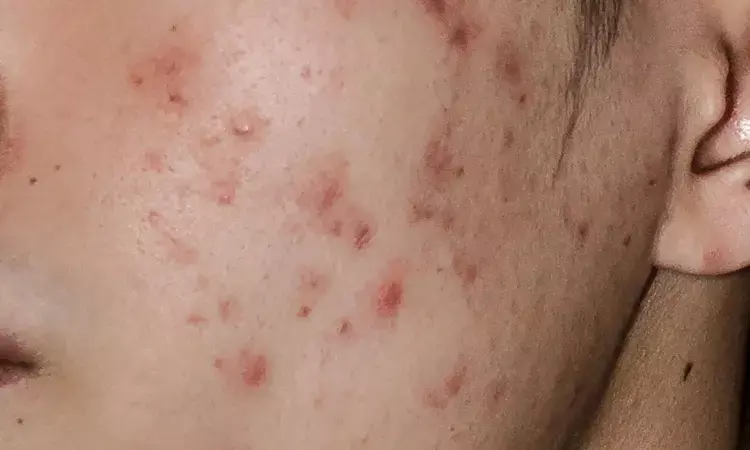
A recent study published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology validated the efficacy and safety of low-dosage isotretinoin as a treatment for acne in Chinese patients, shedding light on a relatively unexplored facet of dermatological care.
Acne vulgaris, a prevalent skin condition worldwide, often poses challenges for patients seeking effective and side-effect-minimized treatments. The study, involving 388 participants undergoing low-dosage isotretinoin therapy, aimed to assess the impact of this approach on Chinese acne patients.
The results revealed a remarkable success rate, with an impressive 90.2% of patients achieving complete remission. The treatment course, spanning an average of 13.5 months, showcased its efficacy across a spectrum of acne severities. Interestingly, the study found that the time to resolution varied among severity groups, indicating nuanced responses to low-dosage isotretinoin.
Post-treatment, a 10.6% relapse rate was observed, emphasizing the need for long-term monitoring. Despite concerns surrounding isotretinoin's side effects, the study provided reassuring findings. Only a minority of patients experienced adverse events, such as hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia, and liver function tests remained within acceptable ranges for the majority.
The research underscores the significance of tailored acne treatments for diverse populations, acknowledging the limited data on low-dosage isotretinoin in the Chinese demographic prior to this study. The positive outcomes suggest a promising avenue for dermatologists and patients seeking effective, well-tolerated acne solutions.
While low-dosage isotretinoin shows promise, the importance of extensive, well-structured clinical trials and continuous monitoring is emphasized. Furthermore, understanding the long-term effects and potential challenges associated with sustained treatment remains crucial.
This study contributes significantly to the evolving landscape of acne treatment, it also provides valuable insights into the benefits and safety of low-dosage isotretinoin, particularly for Chinese patients. As dermatologists consider incorporating this approach into their practice, ongoing research and vigilant patient care will be pivotal in refining acne management strategies.
Source:
Li, Y., Zeng, Y., Chen, Z., Nie, S., & Wu, Z. (2023). The efficiency and safety of low‐dosage isotretinoin therapy for Chinese acne vulgaris patients. In Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology. Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.16073
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


