- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Lower Vitamin D Levels Linked to Increased Severity of Pemphigus Vulgaris: Study
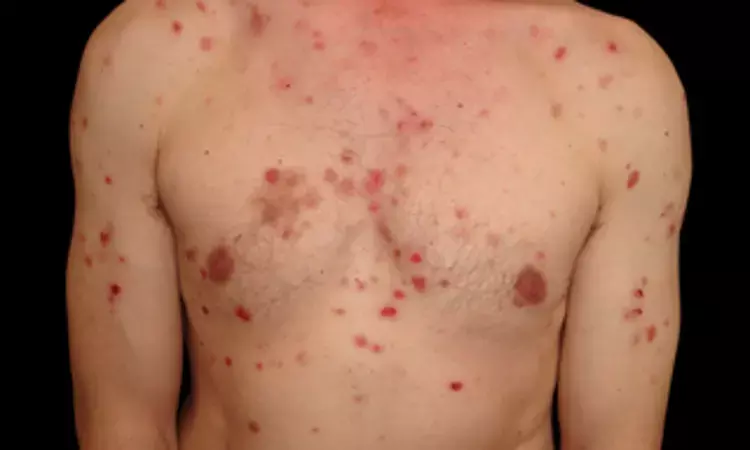
A new study published in The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association found a negative correlation between serum vitamin D levels and the severity of pemphigus vulgaris in a new study thereby suggesting that lower vitamin D levels may be associated with more severe disease manifestations.
Intraepidermal acantholysis is a feature of a group of skin diseases that includes pemphigus vulgaris (PV), a chronic autoimmune bullous condition. Globally, it affects 0.76 to 16.1 people per million. Vitamin D receptors are expressed by both T and B cells, suggesting that vitamin D may play an active role in immunity and immunological regulation. According to studies, calcitriol increases the number of circulating T cells while suppressing the generation of T cell cytokines.
One hormone that helps the body maintain the ideal levels of calcium and phosphorus is vitamin D. It is also a significant immunomodulator, and low vitamin D levels have been linked to a number of autoimmune disorders. Reduced vitamin D levels are frequently observed in numerous communities around the globe. By determining the vitamin D level in PV patients and the relationship between PV and disease severity, the current study aimed to close a gap in the literature.
The patients with pemphigus vulgaris, as determined by histology and direct immunofluorescence, were included in the prospective, cross-sectional study, which was carried out at the Department of Dermatology, Lady Reading Hospital, Peshawar, Pakistan, between December 2021 and June 2022.
To reduce inter-observer bias, a skilled dermatologist evaluated the patients at baseline, and each patient's Pemphigus Disease Area Index score was determined. Using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method, blood samples were extracted from the medial cubital vein and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 minutes at 40°C to determine the serum vitamin D levels. SPSS 22 was used to analyze the data.
Almost, 40 (49.9%) of the 89 patients were male, and 40 (55.1%) were female. 38.48±13.365 years was the average age. 66 patients (74.2%) had vitamin D deficiency, while 7 patients (7.9%) had vitamin D insufficiency. The patients' mean vitamin D level was 17.4882±14.70505 mg/dl. Vitamin D level and illness severity had a negative but non-significant connection (r = -0.131, p = 0.22).
Age, gender, place of residence, socioeconomic position, length of illness, and educational attainment did not significantly correlate with vitamin D insufficiency (p>0.05). Overall, the results of this study indicate a negative relationship between the severity of pemphigus vulgaris and serum vitamin D levels, indicating that more severe disease symptoms may be linked to lower vitamin D levels.
Source:
Paracha, M. M., Khan, A. Q., Sardar, A., Kamal, K., Ikram, A., & Noor, S. M. (2025). Correlation and assessment of vitamin D deficiency with disease severity in patients suffering from pemphigus vulgaris. JPMA. The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association, 75(5), 726–729. https://doi.org/10.47391/JPMA.11552
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


