- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Maternal Alopecia Areata associated with autoimmune, atopic, thyroid, and psychiatric disorders in offsprings:JAMA
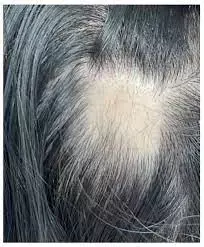
Maternal Alopecia Areata associated with autoimmune, atopic, thyroid, and psychiatric disorders in offsprings suggests anew study published in the JAMA
Alopecia areata (AA) is associated with diverse autoimmune and psychiatric disorders. However, an investigation on the long-term outcomes for offspring born to mothers diagnosed with AA is lacking.
A study was done to investigate the risks for autoimmune, inflammatory, atopic, thyroid, and psychiatric outcomes of offspring born to mothers with AA.
This retrospective population-based birth cohort study used the linked birth registration database with the Nationwide Health Insurance Service database of Korea. The participants included all newborns born to mothers with 3 or more visits with International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision code of L63 and 1:10 birth year, sex, insurance, income, and location of residence–matched control offspring born to mothers without AA during the years from 2003 to 2015. The analysis was conducted from July 2022 to January 2023.
The occurrence of the following diseases was measured in newborns from birth to December 31, 2020: AA, alopecia totalis/universalis (AT/AU), vitiligo, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, asthma, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, Graves disease, Hashimoto thyroiditis, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, mood disorder, and anxiety disorder. Multivariable Cox proportional hazard analyses were performed with the following covariates: birth year, age, insurance type, income level, location of residence, maternal age, mode of delivery, maternal history of atopic disorders, and autoimmune disorders.
Results
In total, 67 364 offspring born to 46 352 mothers with AA and 673 640 controls born to 454 085 unaffected mothers were analyzed. The risk of AA, AT/AU , vitiligo, atopic disorders, hypothyroidism, and psychiatric disorders was significantly increased in offspring born to mothers with AA. Among them, 5088 born to mothers with AT/AU were at much greater risk for the development of AT/AU and psychiatric disorders.
In this Korean retrospective population-based birth cohort study, maternal AA was associated with the development of autoimmune/inflammatory, atopic, thyroid, and psychiatric disorders in their offspring. Clinicians and parents need to be aware of the potential for these comorbidities to occur.
Reference:
Lee JY, Ju HJ, Han JH, et al. Autoimmune, Inflammatory, Atopic, Thyroid, and Psychiatric Outcomes of Offspring Born to Mothers With Alopecia Areata. JAMA Dermatol. Published online May 24, 2023. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2023.1261
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


