- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Metformin decreases risk of basal cell carcinoma: JAAD study
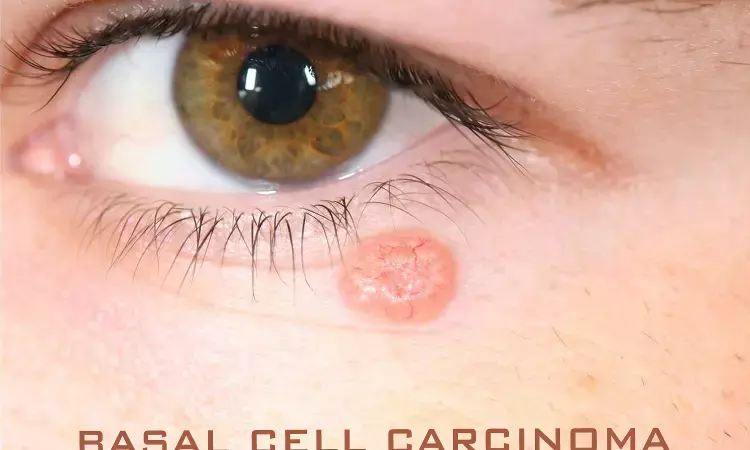
Metformin decreases risk of basal cell carcinoma (BCC), finds Study published in Journal of American Academy of Dermatology.
Metformin, an anti-diabetic drug has been found to decrease the risk of several human malignancies like liver, pancreas, colon and breast.2 A taiwanese retrospective study demonstrated decreased risk of keratinocyte carcinomas in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients on metformin but no differentiation between SCC and BCC was made. Metformin's role in decreasing the risk of BCC was published in a latest study in the Journal of American Academy of Dermatology.
It was a population case-control study in the Icelandic population using Icelandic Cancer Registry (ICR) to delineate the relationship between metformin and the development of BCC, in situ SCC (SCCis), and SCC. A total of 6880 patients with first-time diagnoses of SCCis, SCC, or BCC and 69,620 population controls between 2003 and 2017 were included in the study. Individuals were considered exposed to metformin if they had filled at least 1 prescription of metformin more than 2 years before their diagnosis of keratinocyte carcinoma. Multivariate odds ratios (ORs) were calculated using conditional logistic regression.
Results
In total 4700 individuals with BCC, 1167 with SCCis, and 1013 with invasive SCC were identified and matched with 47,293, 11,961, and 10,367 controls, respectively. Metformin was associated with a lower risk of developing BCC (OR, 0.71; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.61-0.83), even at low doses. No increased risk of developing SCC was observed. SCCis risk was mildly elevated in the 501-1500 daily dose unit category (OR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.00-1.96). Individuals older than 60 years had a decreased risk of BCC with metformin exposure (adjusted OR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.59-0.82).
Study also shows metformin's BCC risk-lowering effect is immediate, with only a low dose being needed to see a clinical benefit. Metformin may have less protective effect in younger individuals <60 years.
Metformin's main antitumor properties are thought to be due to AMP kinase inhibition, leading to the inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin. Its mechanism of inhibition of sonic hedgehog pathway is considered to be the major factor causing decrease in risk of BCC.
In conclusion this study shows an association between decreased risk of BCC and metformin use in a low-UV environment, though the effect may be idiosyncratic only small doses are required to be effective, thereby lowering the risk of side effects due to metformin.
Source-
- Adalsteinsson JA, Muzumdar S, Waldman R, Wu R, Ratner D, Feng H, Ungar J, Silverberg JI, Olafsdottir GH, Kristjansson AK, Tryggvadottir L, Jonasson JG. Metformin is associated with decreased risk of basal cell carcinoma: A whole-population case-control study from Iceland. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021 Jul;85(1):56-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021.02.042.
- Zhang P, Li H, Tan X, Chen L, Wang S. Association of metformin use with cancer incidence and mortality: a metaanalysis. Cancer Epidemiol. 2013;37(3):207-218.
- Tseng CH. Metformin is associated with decreased skin cancer risk in Taiwanese patients with type 2 diabetes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(4):694-700.
MBBS
Dr Manoj Kumar Nayak has completed his M.B.B.S. from the prestigious institute Bangalore medical college and research institute, Bengaluru. He completed his M.D. Dermatology from AIIMS Rishikesh. He is actively involved in the field of dermatology with special interests in vitiligo, immunobullous disorders, psoriasis and procedural dermatology. His continued interest in academics and recent developments serves as an inspiration to work with medical dialogues.He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


