- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Nemolizumab Shows Rapid Efficacy in Treatment-Resistant Chronic Pruritus: Study
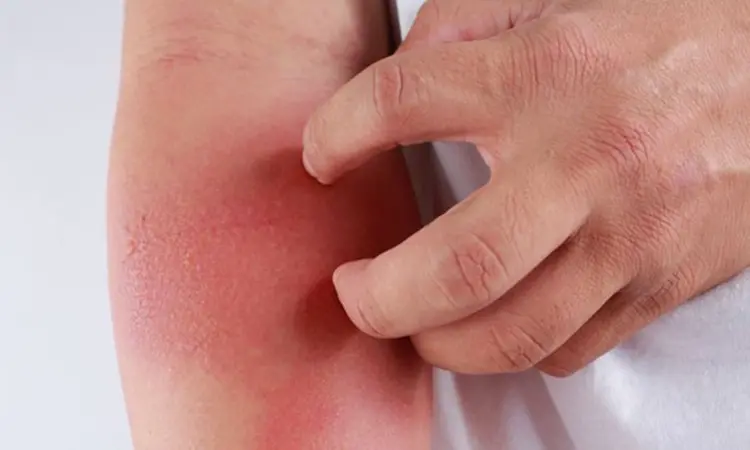
Researchers have found in a new study that Nemolizumab demonstrated rapid and meaningful symptom relief in patients with treatment-resistant chronic pruritus, with a favorable safety profile, including in individuals with significant comorbidities.
Chronic pruritus significantly impacts quality of life and remains challenging to manage, particularly in patients unresponsive to systemic therapies. Nemolizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting the interleukin (IL)-31 receptor, has shown promise in alleviating pruritus across several dermatologic conditions. However, data on its efficacy in treatment-resistant cases, particularly in real-world settings, remain limited.
This case series evaluates the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab in patients with treatment-resistant chronic pruritus. Methods: A multicenter retrospective review was conducted across private dermatology practices and large academic dermatology centers. Patient records were reviewed for demographics, comorbidities, treatment history, and clinical outcomes, including Body Surface Area (BSA), Investigator Global Assessment (IGA), and Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (PP-NRS). Adverse events were recorded.
Results: Twelve patients (5 with atopic dermatitis, 2 with prurigo nodularis, 3 with chronic pruritus of unknown origin, and 2 with concomitant atopic dermatitis and prurigo nodularis) were included. All had previously failed systemic therapies. Mean baseline BSA was 45 percent (range 5–88%), with mean PP-NRS of 9 (range 6–10). After treatment, mean BSA and PP-NRS decreased to 4 percent (11-fold reduction) and 0.9 (10-fold reduction), respectively. Most (10/12) experienced significant pruritus relief within 24 to 72 hours of nemolizumab initiation. No serious adverse events were noted, including in patients with a history of malignancy or end-stage renal disease. Limitations: Small sample size, retrospective design, limited follow-up, and absence of a control group.
Conclusion: Nemolizumab demonstrated rapid and substantial efficacy in treatment-resistant chronic pruritus with a favorable safety profile, even in patients with significant comorbidities.
Reference:
Ruiz Dasilva, D., Soto-González, A., Mollanazar, N. K., Ndubisi, S., Issa, N., Song, J. E., Shahriari, M., Bunick, C. G., Lio, P., Nguyen, H. P., Yosipovitch, G., & Del Rosso, J. Q. (2025). Nemolizumab demonstrates marked efficacy in challenging chronic pruritus: A real-world multicenter case series. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 18(9), 40–46.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


