- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
No benefit of adjuvant leukotriene receptor antagonists with antihistamines in chronic urticaria: Study
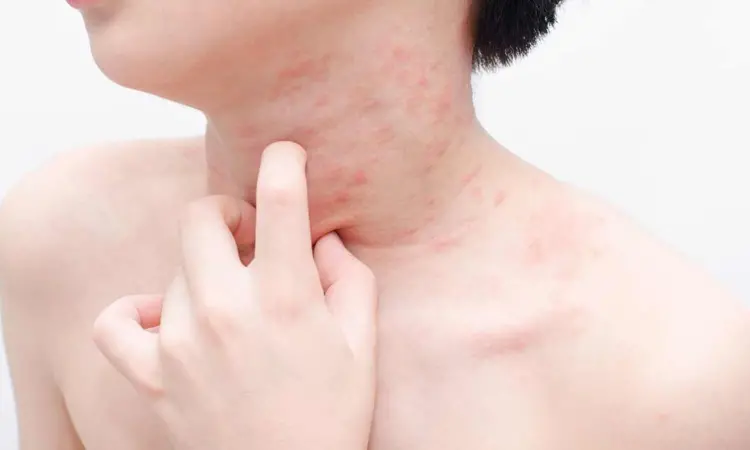
Brazil: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis have shed new light on the potential of leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTAs) as effective adjuvant therapy alongside antihistamines in treating chronic urticaria (CU). The study's findings, published in the International Journal of Dermatology, offer hope for millions worldwide grappling with this debilitating skin condition.
The study findings suggest that leukotriene receptor antagonists with antihistamines do not have better outcomes than antihistamines alone regarding total symptom score (TSS) and pruritus in patients with chronic urticaria.
Chronic urticaria, characterized by persistent and recurrent hives lasting more than six weeks, significantly burdens patients' quality of life. While antihistamines serve as the primary treatment, many patients continue to experience symptoms despite adherence to standard therapies. This has spurred interest in exploring alternative or adjunctive treatments for achieving better symptom control and improved outcomes.
Certain guidelines recommend a second-generation H1-antihistamine (AH) as a first-line treatment for CU patients. However, some patients show insufficient response to a standard dose of this therapy and might benefit from leukotriene receptor antagonist addition. Led by Ocílio Ribeiro Gonçalves, Federal University of Piauí (UFPI), Teresina, Brazil, the systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to compare LTA plus antihistamines with antihistamines alone.
For this purpose, the researchers searched online databases for randomized clinical trial (RCT) data comparing LTA plus AH treatment to AH alone in patients with CU.
The meta-analysis included three studies comprising 234 patients with urticaria. The patients' mean age was 37.23 years in the leukotriene antagonist + antihistamines (LTA + AH) group and 39.14 years in the antihistamines (AH) group. Follow-up ranged from 2 to 18 months between studies.
The study led to the following findings:
- There was no statistically significant difference between groups in terms of TSS level (SMD: −74.82), nor in terms of pruritus (MD: −0.07).
- After sensitivity analysis, with the systematic exclusion of each study from the grouped estimates, the result for TSS level did not change.
In conclusion, the researchers scrutinized the efficacy of combining leukotriene receptor antagonists with second-generation H1-antihistamines (AH) versus AH alone in treating chronic urticaria. They found no significant difference in TSS levels or pruritus between the groups. The results were confirmed by further analysis, suggesting that LTA addition to AH does not yield superior results in CU.
As research in chronic urticaria continues to evolve, the insights gleaned from this meta-analysis pave the way for future investigations into novel therapeutic avenues and optimization of patient care. With a growing understanding of the complex immune mechanisms driving chronic urticaria, the prospect of improved treatment strategies offers hope for better outcomes and enhanced quality of life for affected individuals.
Reference:
Gonçalves, O. R., A. Ribeiro, V. E., L. Galvão, M. T., Silva, S., S. Sobral, M. V., A. Kojima, G. S., R. Freitas, J. L., & Soares, V. G. Leukotriene receptor antagonists as adjuvant therapy of antihistamines in chronic urticaria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Dermatology. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijd.17172
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


