- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Oral naltrexone effective in refractory pruritus in patients with end-stage liver disease;BMJ
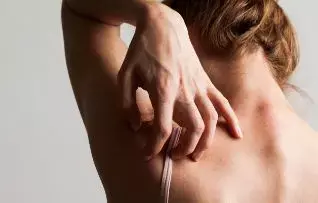
Oral naltrexone therapy helps relieve cholestatic itch,suggests the findings of a recent study published in British Medical Journal ;further elaborating that although it should be used with caution in patients using exogenous opioids for analgesia, it can be considered when treating refractory pruritus in patients with end-stage liver disease.
Cholestatic itch is caused by intrahepatic liver diseases, such as primary biliary cirrhosis and extrahepatic obstruction of the biliary tree, often caused by tumours. The pathophysiology of cholestatic itch is complex and no single treatment has proved definitive. Recent studies show that endogenous opioids in the central nervous system have a role in creating the feeling of pruritus in these patients. Plasma levels of endogenouse opioids including enkephalin increase in patients with chronic cholestasis.
Naltrexone is an opioid receptor antagonist, which reduces central opioidergic tone, believed to be raised in patients with cholestatic pruritus.Previous research has shown that pruritus can be controlled by opioid antagonists such as naloxone. Injection of cholestatic patient's serum to monkey's medulla can cause pruritus that is controlled by naloxone. Several recent studies indicate that opioid antagonists such as naloxone and nalmefene are effective in reducing pruritus in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis.
With this background, the research team undertook the current study to review and assess the efficacy of oral naltrexone for the treatment of cholestatic itch.
This study design consisted of search of electronic databases, grey literature, clinical trials registries and handsearching for studies including naltrexone for cholestatic itch. Full papers were obtained if relevant and studies graded.
Data analysis revealed the following facts.
- Thirteen papers were included in the analysis, including three randomised controlled trials, one controlled clinical trial, one open-label pilot study, seven case reports and one retrospective notes review.
- All studies found naltrexone to be effective in relieving pruritus.
- In all five studies performing statistical analysis, naltrexone significantly reduced pruritus compared with baseline. 37% of patients reported side effects, notably opioid withdrawal-type reactions and recurrence of previous pain, from all pathologies.
FOR FULL ARTICLE FOLLOW THE LINK: https://doi.org/10.1136/
PRIMARY SOURCE: British Medical Journal
Dr Satabdi Saha (BDS, MDS) is a practicing pediatric dentist with a keen interest in new medical researches and updates. She has completed her BDS from North Bengal Dental College ,Darjeeling. Then she went on to secure an ALL INDIA NEET PG rank and completed her MDS from the first dental college in the country – Dr R. Ahmed Dental College and Hospital. She is currently attached to The Marwari Relief Society Hospital as a consultant along with private practice of 2 years. She has published scientific papers in national and international journals. Her strong passion of sharing knowledge with the medical fraternity has motivated her to be a part of Medical Dialogues.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


