- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Oral Roflumilast Shows Promise in Treating Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis: Multicenter Study Highlights Efficacy and Safety
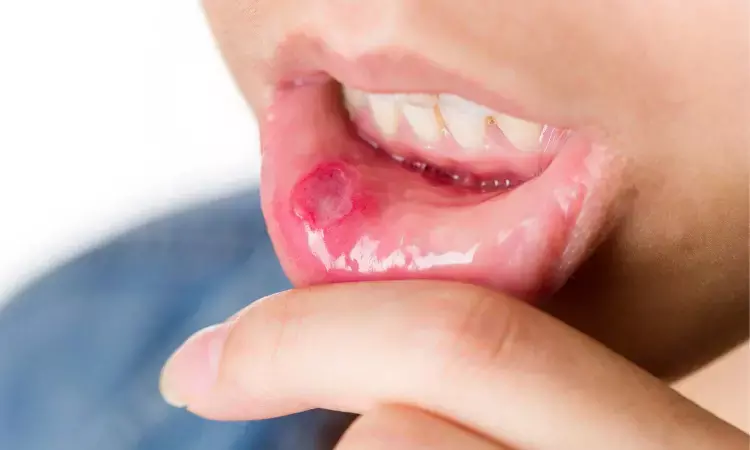
Spain: A multicenter observational study has highlighted the potential of oral roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor, as an effective treatment for recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS).
The study, published in the International Journal of Dermatology, indicates that roflumilast may be an effective treatment for RAS, helping to reduce the frequency and duration of flare-ups and ulcers, and alleviating associated symptoms.
"Additionally, roflumilast is well tolerated at low doses, has a favorable safety profile, and does not necessitate frequent monitoring. Combined with its cost-effectiveness, these benefits position roflumilast as a promising therapeutic option for managing RAS," the researchers wrote.
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis is a condition characterized by painful ulcers in the oral cavity, that often disrupts patients' quality of life due to frequent flare-ups, prolonged healing times, and significant discomfort. RAS poses a therapeutic challenge due to its significant impact on a patient's quality of life. Moreover, there are currently no approved systemic treatments for the condition. Roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, has demonstrated potential in treating other inflammatory dermatological disorders, showing promise for use in RAS.
Against the above background, Rodrigo Peñuelas Leal, Dermatology Department, Consorci Hospital General Universitari de Valencia, Valencia, Spain, and colleagues aimed to evaluate the characteristics, effectiveness, and safety of roflumilast in the treatment of RAS within routine clinical practice.
For this purpose, the researchers conducted a single-cohort ambispective observational study across five Spanish centers involving 22 RAS patients with RAS who were treated with roflumilast. The study collected data on demographic, clinical, and outcome variables. Statistical analysis was performed to compare the outcomes of 12 weeks of roflumilast treatment with a comparable 12-week period before treatment.
The study revealed the following findings:
- During roflumilast treatment, flare-ups (88%) and oral ulcers (94%) significantly reduced compared to the untreated period.
- Pain decreased by 66%, and ulcer duration was shortened by 63%.
- Adverse effects (AEs) were reported in 13 patients, including headache and gastrointestinal disturbances.
- Most AEs were self-limiting or could be managed with dose adjustments.
- Treatment was discontinued in three cases, mainly due to AEs.
The researchers note that the study's small sample size, unblinded design, lack of a placebo, and potential recall bias may affect the results.
"While further research, including long-term and randomized trials with larger patient groups and varying dosages, is needed, these factors suggest that roflumilast could become a safe, effective, and cost-efficient treatment for RAS, benefiting a broader patient population," the researchers concluded.
Reference:
Leal, R. P., Bagan, L., Echevarría, A. G., Peñuelas Ruiz, J. A., Ninet, V. Z., Sánchez Carazo, J. L., Pastor, G. P., Hoyos, C. L., Finello, M., Fernández, S. M., Imbernon, D. B., García, Á. G., Zafrilla, E. P., Cabrera, M. M., & Bagan, J. Treatment of recurrent aphthous stomatitis with oral roflumilast, a multicenter observational study. International Journal of Dermatology. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijd.17478
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


