- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Pemphigus closely associated with increased prevalence and severity of mood disorders
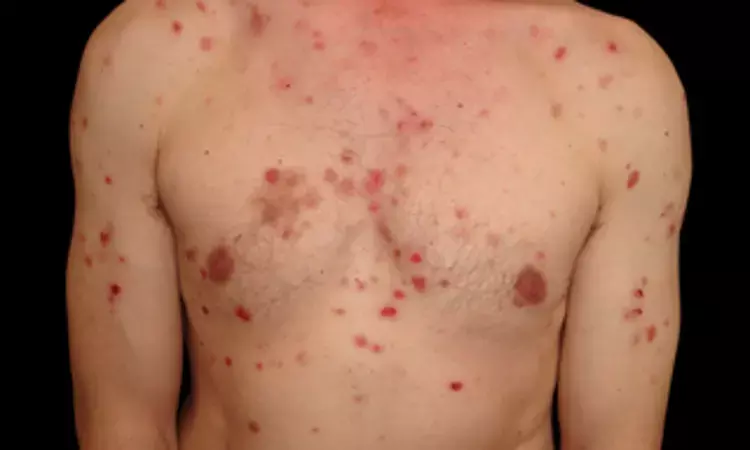
A recent study found the increased psychological impact and mood disorders associated to pemphigus, an autoimmune bullous disease. The findings were published on The Journal of Dermatology. Pemphigus is known for its long disease duration, impact on appearance, social stigmatization, and side effects of treatment, all of which contribute to its significant psychological burden on patients. The study by Jingying Wang and team aimed to shed light on the relationship between mood disorders and pemphigus, which may form a vicious circle, exacerbating the disease.
From March 2020 and January 2022 a total of 140 patients with pemphigus were included in the study, along with a control group of 118 patients with psoriasis. Patients completed several evaluation tools during their visit, including the Beck Anxiety Inventory and Beck Depression Inventory second edition to assess mood disorders, the Dermatology Life Quality Index and the EuroQol Five Dimensions Questionnaire to measure disease-related life quality, and the Visual Analogue Scale to evaluate pain and itching symptoms.
The findings of the study revealed that 30.7% of patients with pemphigus suffered from anxiety disorder (25%) or depressive disorders (14.3%). To ensure accurate comparison, propensity score matching was implemented, resulting in 34 comparable pairs of pemphigus and psoriasis patients.
The analysis showed that pemphigus patients had a significantly higher prevalence and severity of depressive disorders compared to psoriasis patients. However, anxiety disorder levels appeared to be similar between the two groups.
Further analysis using multivariate logistic regression identified several independent risk factors for mood disorders in pemphigus patients. These included disease-related hospitalization history, active mucosal damage, and concomitant thyroid disease.
The study highlights the high prevalence and severity of mood disorders in patients with pemphigus, underscoring the need for increased attention to their psychological well-being. Early identification and proper management of mood disorders in pemphigus patients are essential for improving overall disease management and enhancing their quality of life. The findings also suggest that relevant clinicodemographic indicators can serve as valuable predictors for mood disorders in pemphigus patients. This knowledge can aid physicians in identifying at-risk individuals and providing appropriate support and interventions.
Source:
Wang, J., Wu, H., Cong, W., Zhu, H., Zheng, J., Li, X., & Pan, M. (2023). Psychological morbidity in patients with pemphigus and its clinicodemographic risk factor: A comparative study. In The Journal of Dermatology. Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1111/1346-8138.16875
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


