- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Platelet-rich plasma effective treatment option for venous ulcers: Study
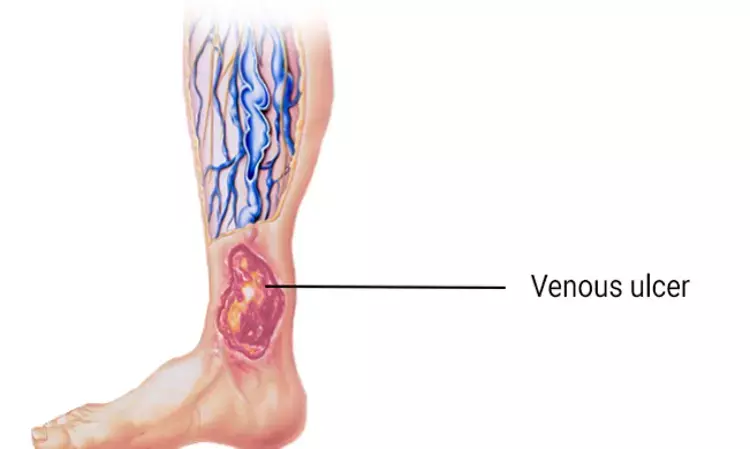
A new review study published in the recent issue of the Wound Repair and Regeneration journal found study data to support the use of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in the treatment of venous ulcer patients. Ulcers or chronic wounds are skin breaches that often reoccur and either do not heal at all or take a very long period to cure. Numerous ulcer forms, including venous, arterial, diabetic, pressure, and traumatic ulcers, can be classified as non-healing ulcers. The most prevalent type of chronic ulcers affecting the lower extremities among all of them are venous ulcers, which have a major effect on both job productivity and quality of life. In the population over 60, the prevalence of chronic venous insufficiency ranges from 1% to 2%. In the past, anatomical processes of valvular incompetence were the main focus of research on venous reflux illness. Recent studies on the cellular and molecular causes of venous insufficiency have demonstrated that the illness is a multifaceted, intricate process that reflects both cellular inflammatory response and systemic anomalies in connective tissue formation.
PRP, or autologous platelet rich plasma, is a blood-derived substance that is becoming more and more popular in therapeutic settings. Among its many uses, PRP has replaced traditional dressings for the treatment of chronic ulcers. Thus, this study by Tianbo Shi and colleagues was to assess the clinical evidence supporting the use of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of venous ulcers (VUs). Electronic searches utilized Web of Science, Embase, PubMed, and the Cochrane Library data and to evaluate the methodological quality, AMSTAR-2 was employed. The GRADE method was used to evaluate the quality of the evidence. Due to the constraints of entries 2, 4, and 7, AMSTAR-2 determined that the methodological quality of the included reviews was usually insufficient. The outcome of the measures through evidence of quality was insufficient because of bias risk and imprecision.
Many studies document the effective use of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of venous ulcer patients. The efficacy of platelet-rich plasma appears to be supported by the data, despite this study also highlights a number of shortcomings. However, given the methodological shortcomings of the included systematic reviews and meta-analyses, these findings requires caution in interpretation.
Reference:
Shi, T., Hu, S., Hui, J., Ji, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2024). An overview of systematic reviews of clinical studies of platelet‐rich plasma for venous ulcers. In Wound Repair and Regeneration. Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1111/wrr.13201
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


