- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Risankizumab improves long-term outcomes in patients with palmoplantar pustulosis: Study
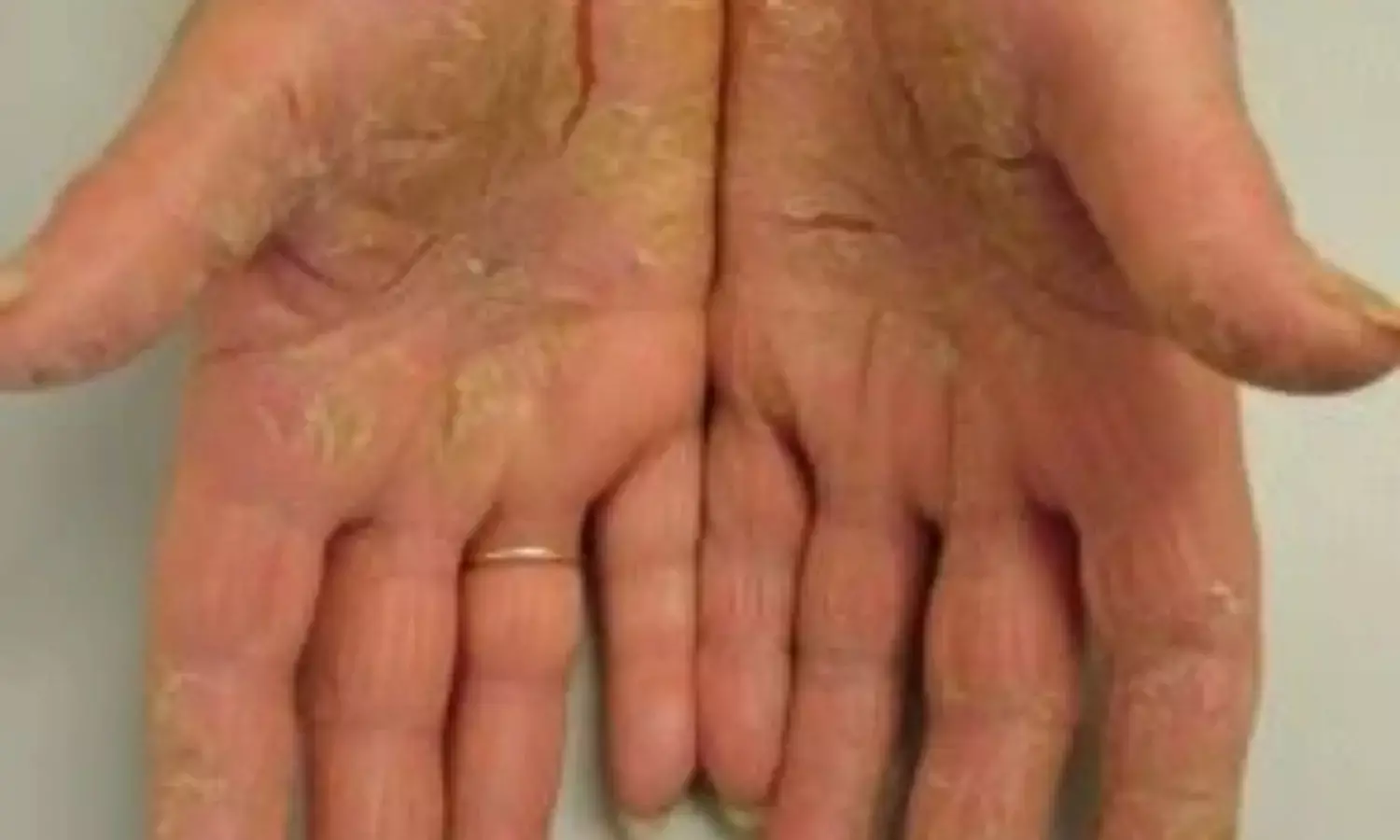
A new study published in The Journal of Dermatology revealed that patients with palmoplantar pustulosis (PPP) who were 18 years of age or older who received risankizumab therapy saw long-lasting improvements in their disease's signs and symptoms, and their safety profile was similar with previous safety findings from other psoriasis risankizumab trials.
Palmoplantar pustulosis is typified by recurrent flare-ups and remissions and mostly affects women, and patients frequently have a history of localized infection and smoking. According to estimates, the prevalence of PPP in the Japanese population is 0.12%, greater than that of other affluent nations. Up to 30% of individuals with PPP (mostly women) have pustulotic arthro-osteitis (PAO) which is a serious comorbidity.
A humanized immunoglobin G1 monoclonal antibody called risankizumab (RZB) binds to the p19 component of IL-23 to selectively block it. Psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis vulgaris, erythrodermic psoriasis, generalized pustular psoriasis, and PPP in adults are among the conditions for which it is authorized in Japan. From the JumPPP research, this investigation was set to assess RZB in adult Japanese subjects with moderate-to-severe palmoplantar pustulosis.
This study reports the safety and effectiveness of risankizumab, an interleukin 23 p19 inhibitor. At weeks 0 and 4, participants were randomized 1:1 to receive RZB (150 mg) or a placebo. And, from week 16 to week 52 (for patients first assigned to RZB) or week 56 (for patients initially randomized to placebo), all patients received RZB. A Palmoplantar Pustulosis Area and Severity Index (PPPASI) change from baseline was the main outcome, and at week 16, there was a ≥50%/≥75% improvement in PPPASI (PPPASI 50/75). Safety and efficacy were assessed at 76 and 68 weeks, respectively.
A total of 119 individuals were recruited (n = 61 for RZB and n = 58 for placebo). The substantial difference in PPPASI change from baseline at week 16 indicated greater improvement with RZB when compared to placebo. At week 16, a higher percentage of patients who received RZB than those who received a placebo attained PPPASI 50, but not PPPASI 75. In general, improvements persisted until week 68.
The safety profile was mostly in line with other research on RZB's effects on psoriasis. Overall, in Japanese patients with PPP, RZB was shown to be more effective than a placebo at week 16, and benefits persisted until week 68. It was also well tolerated and showed no unanticipated safety effects.
Source:
Okubo, Y., Murakami, M., Kobayashi, S., Tsuji, S., Kishimoto, M., Ikeda, K., Jibiki, M., Neimark, E., Padilla, B., Shen, J., Peters, S., & Terui, T. (2025). Risankizumab in Japanese patients with moderate‐to‐severe palmoplantar pustulosis: Results from the randomized, phase 3 JumPPP study. The Journal of Dermatology. https://doi.org/10.1111/1346-8138.17659
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


