- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Some antihypertensive medications increase risk of psoriasis, find studies
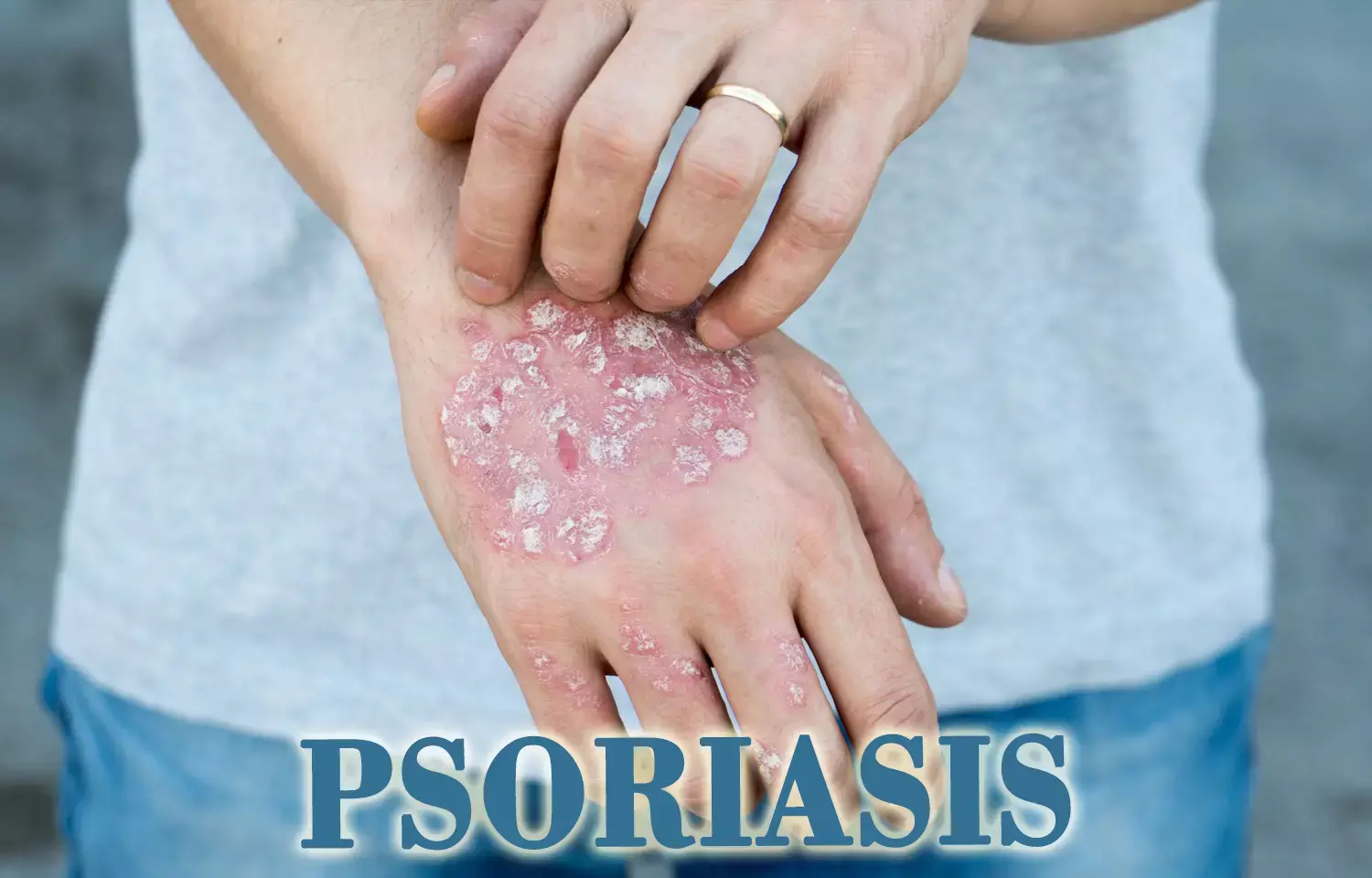
Use of antihypertensive mediations and the development of psoriasis, finds analysis of some published studies.The studies indicated that angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors, beta- blockers, calcium-channel blockers, and thiazide diuretics may increase the risk of psoriasis.Therefore, antihypertensive drug users should be carefully monitored for psoriasis.
The analysis is published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.
Diverse genetic and/or external factors may induce psoriasis. Drug exposure is 1 such prominent external factor; antihypertensive drugs are reportedly associated with psoriasis, but study results have been inconsistent. In this context, we investigated the associations between antihypertensive drugs and incidence if psoriasis via a systematic literature review and meta-analysis.
The researchers carried out literature search in databases such as PubMed, Embase and Web of Science was conducted on 8 January 2021, and obtained data were pooled for meta- and network meta-analysis. Fixed- or random effect models were used to calculate odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for evaluating the strength of the associations between antihypertensive drugs and psoriasis incidence. In addition to meta-analysis, Bayesian network meta-analysis was performed.
In the meta analysis, thirteen eligible studies were included for meta-analysis with 6 378 116 individuals and 8 studies for network meta-analysis with 5 615 918 individuals. All antihypertensive drugs were significantly associated with psoriasis incidence. In a meta-analysis, the pooled ORs were 1.67 for angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, 1.40 for β-blockers, 1.53 for calcium-channel blockers (CCBs), and 1.70 for thiazide diuretics.
The authors of the analysis propose several mechanisms by which blood pressure medications may affect an individual's risk of developing skin conditions.
The study confirmed the associations between antihypertensive drugs and psoriasis; ACE inhibitors, BBs, CCBs and thiazide diuretics increased the risk of psoriasis.
"Our findings indicate that patients who take antihypertensive drugs should be carefully monitored for psoriasis," said senior author Hye Sun Gwak, PharmD, PhD, of Ewha Womans University, in Seoul.
For further reference log on to:
https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bcp.15060
Hina Zahid Joined Medical Dialogue in 2017 with a passion to work as a Reporter. She coordinates with various national and international journals and association and covers all the stories related to Medical guidelines, Medical Journals, rare medical surgeries as well as all the updates in the medical field. Email: editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


