- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Suitable skin hygiene habits help reduce pruritus of hands and pain in individuals with hand eczema
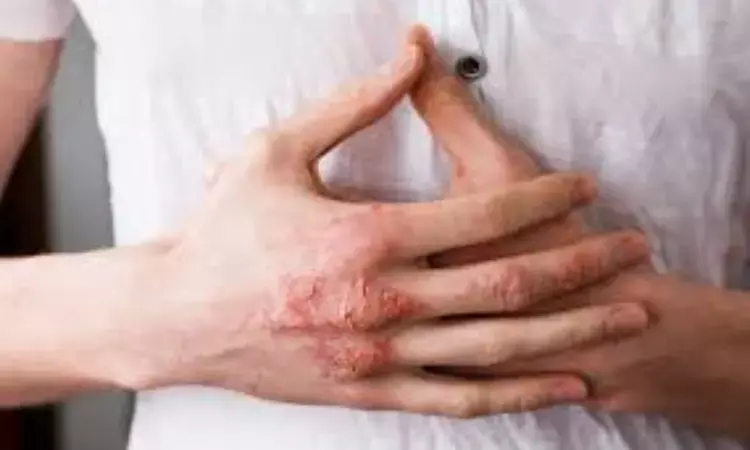
China: Pruritus of the hands and pain can be reduced by considering and promoting suitable skin hygiene practices in the follow-up and treatment of patients with hand eczema, a recent study has revealed. The findings were published online in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology on November 01, 2023.
Hand eczema (HE) is a common inflammatory skin disorder primarily located on the hands and wrist. Among several symptoms of HE, pain and itch are burdensome and prevalent. However, not much research has been performed on the associations between skin hygiene habits and the severity of pain and itch among HE patients. Therefore, Ziye Yang, Department of Dermatology, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China, and colleagues investigated the relationship between skin hygiene habits and itch and pain severity in patients with hand eczema in a cross-sectional study.
The study was conducted at five universities situated in five geographically dispersed cities: Wuhan, Changsha, Urumqi, Xiamen, and Hohhot. All freshmen who gave informed consent underwent a skin examination and completed an online questionnaire during September and October 2018.
The researchers gathered participants' skin hygiene habits for the past two years through the questionnaire, including the duration, frequency, and water temperature of baths during the autumn and spring seasons, as well as the most frequently used hand washing cleaners routinely and daily frequency of hand washing.
The researchers led to the following findings:
- Increased frequency of hand washing and bathing had a significant association with higher itch and pain numerical rating scale (NRS) scores after adjusting for potential confounders.
- Compared with the use of water for washing hands, the use of hand sanitiser was associated with a higher NRS pain score.
"Promoting and considering suitable skin hygiene practices in the follow-up and treatment of patients with hand eczema can help reduce pruritus of the hands and pain," the researchers concluded.
Reference:
Chen, P., Yang, Z., Li, J., Shen, M., Chen, X., & Xiao, Y. Association between skin hygiene habits and the intensity of itch as well as pain in hand eczema: A cross-sectional study. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.19618
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


