- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Topical berdazimer gel safe and effective therapy for molluscum contagiosum: JAMA
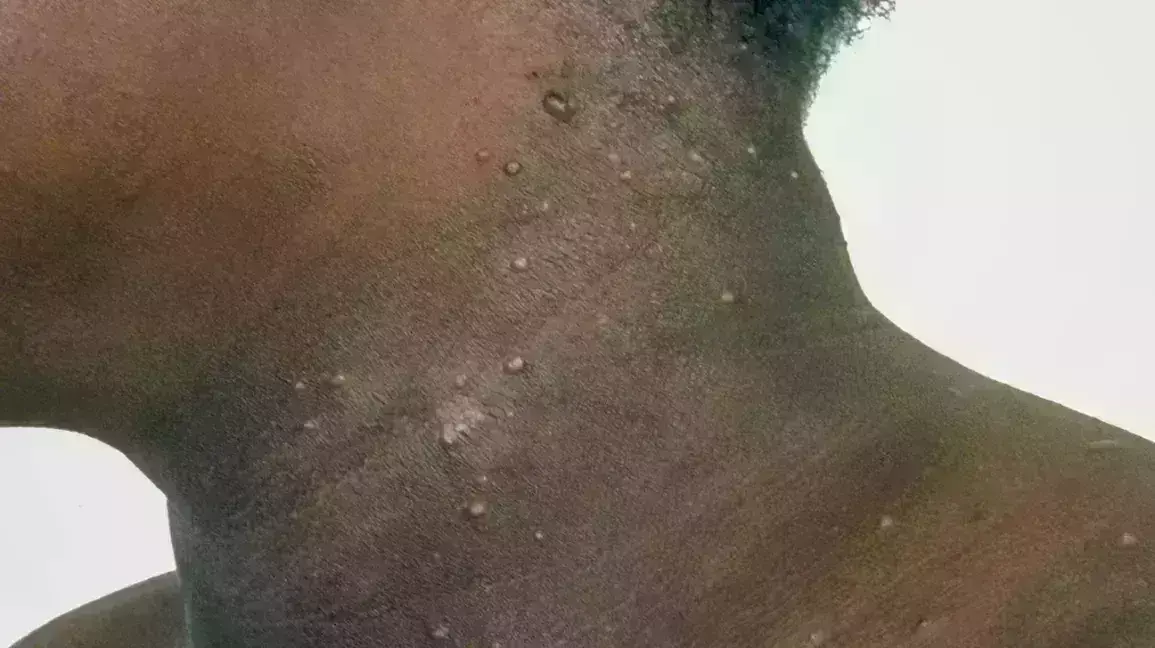
Topical berdazimer gel is a safe and effective therapy for molluscum contagiosum according to a recent study published in the JAMA Dermatology.
Molluscum contagiosum (MC) is a highly contagious skin condition. Lesions may persist for months to years, and no US Food and Drug Administration–approved medications are currently available in the US.
A study was conducted to assess the efficacy and safety of berdazimer gel, 10.3%, a novel topical nitric oxide-releasing medication, in the treatment of Molluscum contagiosum.
This was a multicenter, vehicle-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 randomized clinical trial (B-SIMPLE4) conducted in 55 clinics (mostly dermatology and pediatric) in the US from September 1, 2020, to July 21, 2021. Eligible participants were 6 months or older and had from 3 to 70 raised MC lesions. Patients with sexually transmitted Molluscum contagiosum or with Molluscum contagiosum only in the periocular area were excluded.
Patients were randomized to treatment with berdazimer gel, 10.3%, or vehicle gel, applied as a thin layer to all lesions once daily for 12 weeks. The primary efficacy end point was complete clearance of all MC lesions at week 12. Safety and tolerability measures included adverse event frequency and severity, and assessment of local skin reactions and scarring. Data analyses were performed from August 31, 2021, to September 14, 2021.
The Results of the study are:
- A total of 891 participants were randomized, 444 to berdazimer, 10.3% and 447 to vehicle
- In the intention-to-treat population, 88.5% (393 patients) in the berdazimer group and 88.8% in the vehicle group had a lesion count performed at week 12.
- At week 12, 32.4% (144 patients) in the berdazimer group achieved complete clearance of MC lesions compared with 19.7% (88 patients) in the vehicle group with 14.4% (64 patients) of the berdazimer group discontinuing treatment because of Molluscum contagiosum clearance compared with 8.9% (40 patients) of the vehicle group.
- Adverse event rates were low.
- The most common adverse events were application-site pain and erythema, mostly mild in severity. Adverse events leading to discontinuation affected 4.1% (18 patients) of the berdazimer group and 0.7% (3 patients) of the vehicle group.
- The most common local skin reaction was mild to moderate erythema.
Thus, use of berdazimer gel, 10.3%, for MC appears to demonstrate favorable efficacy and safety with low adverse event rates.
Reference:
Browning JC, Enloe C, Cartwright M, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Topical Nitric Oxide−Releasing Berdazimer Gel in Patients With Molluscum Contagiosum: A Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Dermatol. Published online July 13, 2022. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.2721
Keywords:
Efficacy, Safety, Topical, Nitric Oxide, Releasing, Berdazimer, Gel, Patients, Molluscum, Contagiosum, jama dermatology, John C. Browning, Carolyn Enloe, Martina Cartwright, Adelaide Hebert, Amy S. Paller, David Hebert, Elaine Kearney Kowalewski, Tomoko Maeda-Chubachi
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


