- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Vitamin D Supplements Improve Hair Regrowth in patients with Diffuse Hair Loss: Study
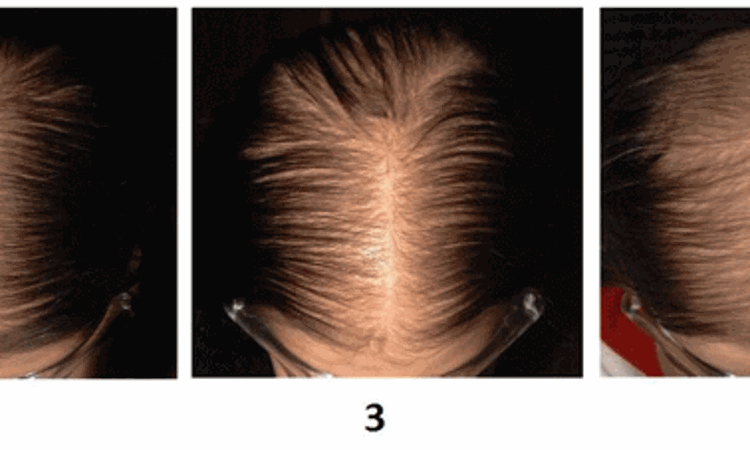
Micronutrients, including vitamins, play an important role in cellular multiplication and development in the matrix cells in the hair follicle bulb. A recent study suggests that the use of oral vitamin D3 (200,000 IU, fortnightly) for 3 months resulted in significant improvement in hair regrowth in the patient of TE. The study findings were published in the Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology on February 28, 2021.
Telogen Effluvium (TE) is non-scarring alopecia and becomes acute when occurs at 2-3 months after the triggering events. Vitamin D receptors are found in every cell of the body and have been shown to play a role in bone, neural, and cardiovascular health; immune regulation; and possibly cancer prevention via the regulation of cell differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. Although it is controversial, vitamin D deficiency has been associated with various forms of nonscarring hair loss, including telogen effluvium, androgenetic alopecia, and alopecia areata. To fill the knowledge gap, researchers of the Nishtar Medical University, Multan, conducted a study to estimate the prevalence of telogen effluvium (TE) and to evaluate the efficacy of vitamin D in the treatment of this problem in women belonging to various cities of south Punjab, Pakistan.
In the present study, researchers included a total of 40 adult women suffering from the problem of TE. Each woman was treated with oral vitamin D3 (200,000 IU) therapy fortnightly and a total of 6 doses were given to each patient. After 15 d of the last dose, researchers assessed the clinical condition of patients and the level of satisfaction was to treatment was recorded.
Key findings of the study:
• Upon evaluation, researchers observed that the patients between 21–30 y of age were found to be more frequently affected with TE compared to 35% of females of age 31–40 y.
• They found a significant improvement in hair growth in young (r=0.457 p<0.003) women and in those, which do not use sunscreen (r=−0.331 p<0.037) but commonly utilize milk or milk protein (r=−0.311 p<0.051).
•They also found that Vitamin D3 therapy resulted in the improvement of the condition in 82.5% of patients of TE.
• They noted that the use of oral vitamin D3 (200,000 IU, fortnightly) for 3 months resulted in significant improvement in hair regrowth in the patient of TE.
The authors concluded, " The overall response to oral vitamin D3 therapy was satisfactory (85%) in terms of hair regrow. The result showed improvement in hair growth in young women those do not use sunscreen but commonly utilize milk or milk protein."
They further added, "Large double-blind, placebo-controlled studies are required to determine the role of vitamin D supplementation and its relationship with micronutrients necessary to avoid occurrence to TE."
For further information:
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jnsv/67/1/67_68/_article
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


