- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Frontal fibrosing alopecia from a clinician's perspective: JAAD
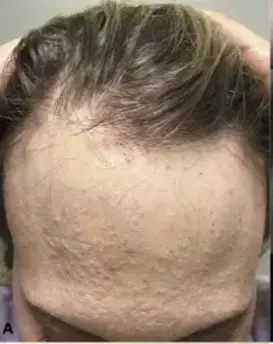
Source- Pham, C. T., Hosking, A. M., Cox, S., & Mesinkovska, N. A. (2020). Therapeutic response of facial papules and inflammation in frontal fibrosing alopecia to low-dose oral isotretinoin. JAAD case reports, 6(5), 453–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.01.030
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) is a scarring alopecia of the frontotemporal scalp, considered a variant of lichen planopilaris seen commonly in postmenopausal women. Eyebrow alopecia is most commonly associated but axillary, pubic, face and extremities may be involved. Perifollicular inflammation may be clinically evident.
Hormonal factors, autoimmunity, genetic susceptibility and exogenous factors have been implicated in its pathogenesis. It is a T helper cell type 1 (Th1) reaction targeting the infundibulum and isthmic region of hair follicle damaging the bulge area which is the niche of follicular stem cells. Downregulation or abnormal function of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ), pivotal for healthy pilosebaceous units has been implicated in lichen planopilaris. Dehydroepiandrosterone is essential for the stimulation of PPAR-γ which explains the efficacy of 5α-reductase inhibitors in FFA.
Study by Pindado-Ortega et al demonstrated statistically significant stabilization rate of Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) after 12 months in dutasteride group (n = 148) compared to other systemic therapies (hydroxychloroquine, doxycycline, and istotretinoin, n = 20) and without systemic treatment (n = 56). Role of facial moisturizers, sunscreens and other skin or hair care products in pathogenesis of Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) is controversial.
According to latest systematic review on FFA, topical and intralesional corticosteroids are often used as first-line therapies because of their minimal side-effect profile.2 Hydroxychloroquine and 5a-reductase inhibitors (dutasteride or finasteride) were stated to be the most effective therapies. 2
In conclusion, FFA is a disease with increasing prevalence so knowledge about is essential but at the same time further studies are required to understand the pathogenesis, develop a Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) severity scale and treat the disease.
Source-
- Heymann WR. Confronting frontal fibrosing alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021 Aug;85(2):319-320. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021.05.015
- Dina Y, Aguh C. An algorithmic approach to the treatment of frontal fibrosing alopecia-a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2018.10.043.
MBBS
Dr Manoj Kumar Nayak has completed his M.B.B.S. from the prestigious institute Bangalore medical college and research institute, Bengaluru. He completed his M.D. Dermatology from AIIMS Rishikesh. He is actively involved in the field of dermatology with special interests in vitiligo, immunobullous disorders, psoriasis and procedural dermatology. His continued interest in academics and recent developments serves as an inspiration to work with medical dialogues.He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


