- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Intensive insulin therapy may aggravate pre-existing diabetic retinopathy: Case Report
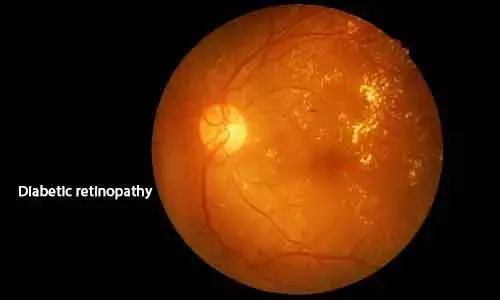
China: A recent case study, published in the journal Medicine, describes the case of a type 2 diabetes female patient who experienced rapid progression of high-risk proliferative diabetic retinopathy after receiving the insulin intensive therapy (IT).
The case in question is of a 58-year-old type 2 diabetes female patient suffered a rapid and dramatic decline of vision acuity in the left eye in 2 months after the insulin IT. However, the best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) of her right eye, which was in much severer condition and received panretinal photocoagulation (PRP) before, improved after the IT.
The patient received intravitreal injection of conbercept (IVC) to her left eye, and 5 days later, underwent pars plana vitrectomy (PPV), combined with PRP and silicon oil injection.
The postoperative BCVA of the left eye was 20/200 and improved to 20/160 one month later. During the subsequent 2 months of follow-up, her BCVA remained 20/160 in both eyes. Her blood glucose level also remained stable.
"Insulin IT for untreated proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) patients can cause severe and irreversible consequences, so for such patients, the conservative treatment for glycemic control may be much safer. But if insulin IT is inevitable, the patient should undergo PRP promptly before the IT, and close eye monitoring during the IT is also essential," concluded the authors.
About Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a leading cause of irreversible blindness in the world. It has been proven in some studies that intensive treatment (IT) to reduce glycemic levels, can slow down the progression of DR in both type 1 and 2 diabetes in the long-term development. Therefore, near-normalization of blood glucose level is a major target of DR monitoring. However, since first being noticed in 1983, clinical trials have demonstrated that insulin IT can cause a paradoxical early aggravation of DR called " early worsening of diabetic retinopathy" (EWDR) in type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Most patients at baseline in these studies were with minimal-to-moderate non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) or even without DR. And the cases of EWDR caused by insulin IT at a baseline of high-risk proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) in type 2 diabetes patients were barely reported.
The case report titled, "Rapid progression of high-risk proliferative diabetic retinopathy induced by insulin intensive therapy," is published in the journal Medicine.
DOI: https://journals.lww.com/md-journal/Fulltext/2021/02190/Rapid_progression_of_high_risk_proliferative.10.aspx
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


