- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Acupuncture may Improve Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes: Study
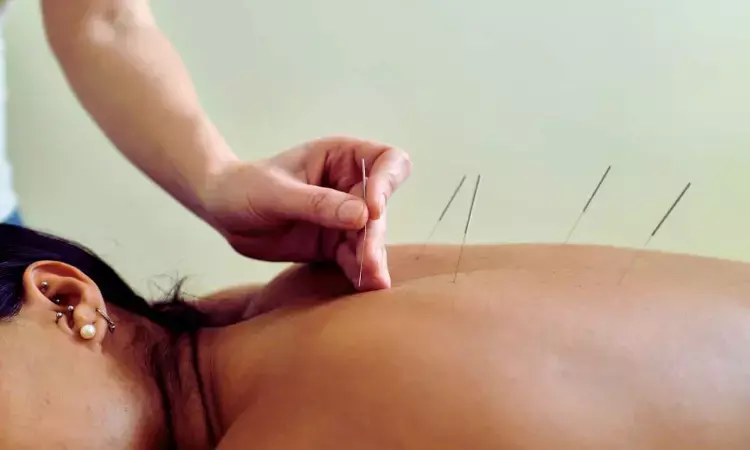
A new study published in the Postgraduate Medical Journal showed that acupuncture significantly reduces FBG, HbA1c, 2hPG, and HOMA-IR in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), though it shows no major effect on insulin levels. The findings suggest acupuncture as a valuable complementary therapy for glycemic control.
Therapies, like medication and lifestyle changes, are frequently successful in T2DM patients but could not completely regulate blood sugar levels or avoid side effects. Traditional Chinese Medicine, acupuncture has drawn increasing attention as an adjunctive strategy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It is thought to promote pancreatic β-cell activity, increase insulin sensitivity, and control the autonomic nervous system.
According to recent research, acupuncture may improve glycemic management by influencing lipid profiles, glucose metabolism, and inflammatory markers. Additionally, it provides a non-pharmacological substitute that might lessen reliance on prescription drugs. Examining the effectiveness and processes of acupuncture in type 2 diabetes may offer important information on how to combine conventional and contemporary medical procedures for better diabetic care. This study assessed how acupuncture affects T2DM outcome variables connected to blood glucose.
From the beginning until July 3, 2025, this research examined 4 databases (PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library) to find randomized controlled studies that compared acupuncture with non-acupuncture and recruited patients with type 2 diabetes. Prediction Intervals (PI) for every outcome were included in the study, along with normalized mean differences with 95% CI. Additionally, sensitivity analysis, meta-regression, subgroup analysis, and publication bias assessment were carried out.
There were 20 RCTs with 1479 subjects. Where FBG (SMD: -0.52; 95% CI: -0.91 to -0.13; P = 0.009), HbA1c (SMD: -0.76; 95% CI: -1.24 to -0.27; P = 0.002), 2hPG (SMD: -0.69; 95% CI: -1.00 to -0.39; P < 0.00001), and HOMA-IR (SMD: -1.72; 95% CI: -2.57 to -0.86; P < 0.0001) were all significantly lower in the acupuncture group.
However, there was no statistically significant difference in the insulin level (SMD: -1.16; 95% CI: -2.36 to 0.04; P = 0.06). Overall, in T2DM patients, acupuncture successfully lowers FBG, HbA1c, 2hPG, and HOMA-IR; however, insulin levels are not much impacted. Future studies have to concentrate on refining acupuncture procedures, evaluating its long-term impacts, and examining the molecular processes behind its influence.
Reference:
Li, N., Xu, G., Lin, J., Li, H., He, X., Huang, J., Du, X., Xiang, Z., Shi, Z., & Wang, Y. (2025). Effect of acupuncture for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Postgraduate Medical Journal, qgaf132. https://doi.org/10.1093/postmj/qgaf132
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


