- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
AI may help predict risk of disease progression in patients with diabetic retinopathy
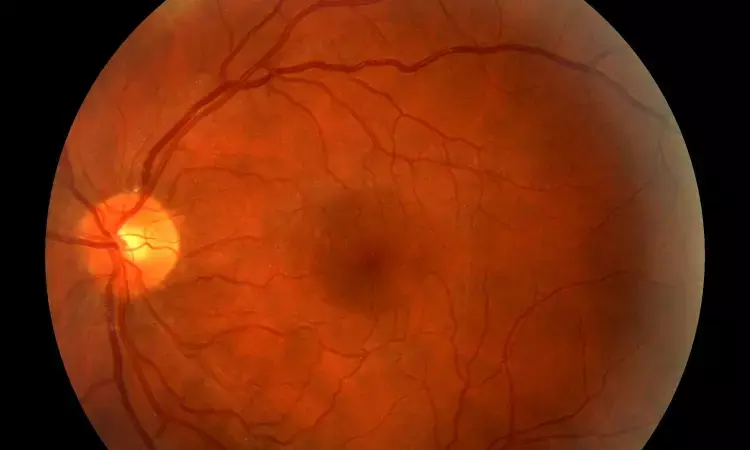
USA: For people with diabetic eye disease, one of the most difficult and important tasks is estimating the risk of diabetic retinopathy (DR) progression. A recent study published in the journal Diabetes has shed light on dentifying the risk of the progression of diabetic retinopathy using machine learning on ultrawide field retinal images.
The study findings, presented at the 83rd American Diabetes Association Scientific Sessions (ADA 2023), demonstrated the feasibilty and accuracy of using machine learning models for identification of DR progression using ultrawide field (UWF) retinal images. The artificial intelligence prediction for about 91% of the images were either correct labels; or the labels showed greater progression than the original labels.
"The use of machine learning algorithms may further refine the risk of disease progression and personalize screening intervals that may improve vision-related outcomes and reduce costs," the researchers wrote in their study.
Current scales of diabetic retinopathy severity have informed clinicians on the progression risk and provided recommendations for treatment and follow-up. Using AI (artificial intelligence) algorithms may improve in this process. In the study, Amber Nigam, Boston, MA, Cambridge, MA, and colleagues developed and validated machine learning models for DR progression from UWF retinal images. They were labeled for baseline DR severity and progression on the basis of clinician review of the images and 3-year longitudinal follow-up using the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) severity scale.
The dataset consisted of eight classes: proliferative DR (16.55%), severe NPDR progression (11.27%) /nonprogression (10.68%), Moderate NPDR progression (10.1%) /nonprogression (15.85%), Mild nonproliferative DR (NPDR) progression (10.16%) /nonprogression (10.73%), and no DR nonprogression (14.62%). Based on 60-20-20 proportions, 9970 unique images were split into the train, the validation, and the test datasets.
Study’s key findings include:
- The ResNet model fine-tuned on this dataset has a classification test accuracy of 81% and an AUC of 0.967 on the test dataset.
- The objective of the model is to reduce false negatives, which refers to predicting a class that is less progressive than the true label.
- The predicted labels for 91% of the images were either correct labels or were the labels with greater progression than the original labels.
The researchers suggests that the use of machine learning algorithms may further refine the risk of disease progression and personalize screening intervals that may reduce costs and improve vision-related outcomes.
Reference:
AMBER NIGAM, JIE SUN, VARSHINI SUBHASH, PAOLO S. SILVA; 26-LB: Identifying the Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy Progression Using Machine Learning on Ultrawide Field Retinal Images. Diabetes 20 June 2023; 72 (Supplement_1): 26–LB. https://doi.org/10.2337/db23-26-LB
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


