- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Bariatric surgery increases risk of low blood sugar in obese diabetics: Study
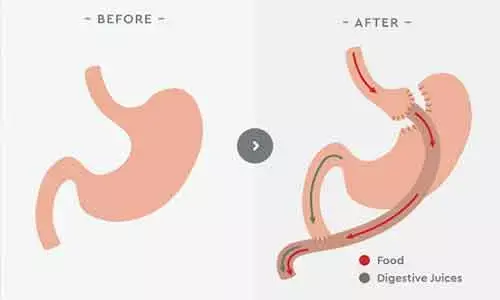
UK: Obese patients with diabetes undergoing gastric bypass surgery are at increased risk of developing low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) post-surgery, suggests a recent study in the journal Diabetes Care. Postbariatric hypoglycemia could be due to a combination of increased glycemic variability (GV), increased GLP-1 response, and reduced levels of mean glucose.
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) is an established treatment for obesity and type 2 diabetes. Ibiyemi Ilesanmi, Imperial College London, London, U.K, and colleagues aimed to establish the effect of RYGB on GV and hypoglycemia in this prospective observational study of 10 patients with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes and obesity.
The patients were studied before RYGB and 1 month, 1 year, and 2 years postsurgery with continuous glucose measurement (CGM). A mixed-meal test (MMT) was conducted at Pre, 1 month, and 1 year.
Key findings of the study include:
- After RYGB, mean CGM decreased (at 1 month, 1 year, and 2 years), and GV increased (at 1 year and 2 years).
- Five of the 10 participants had a percent time in range (%TIR) <3.0 mmol/L (54 mg/dL) greater than the international consensus target of 1% at 1 or 2 years.
- Peak glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucagon area under the curve during MMT were positively and negatively associated, respectively, with contemporaneous %TIR <3.0 mmol/L.
"Our findings demonstrate that patients undergoing RYGB are at risk for development of postbariatric hypoglycemia due to a combination of reduced mean glucose level, increased GV, and increased GLP-1 response," concluded the authors.
"Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Increases Glycemic Variability and Time in Hypoglycemia in Patients With Obesity and Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective Cohort Study, is published in the journal Diabetes Care.
DOI: https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/early/2020/12/14/dc20-1609
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


