- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Blood Ketone Testing More Effective for Gestational Diabetes Monitoring: Study
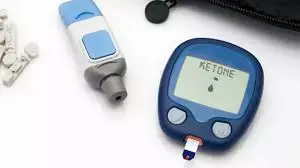
A new study published in the journal Hormones has revealed that blood ketone testing is more effective than urine tests for detecting ketosis in women with gestational diabetes.
Women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) are frequently asked to check their ketone levels by measuring ketonuria before breakfast. However, ketosis could be present even before lunch and dinner. Furthermore, blood ketone measurement could be a more accurate test.
The aim was to evaluate the effect of a blood ketone intensive measurement in the detection of ketosis in women with gestational diabetes mellitus with a negative urinary ketone test. This was a single center, observational, prospective study involving consecutive women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Only women with negative fasting urinary ketone tests were included. During the same gestational weeks (weeks 30–32), all women were asked to perform a blood ketone test before their main meals. Ketosis was defined as the presence for at least 25% of the time of fasting blood ketone levels > 0.1 mmol/L and > 0.2 mmol/L before lunch and dinner.
Results: Overall, a total of 101 women (mean age 34.7 ± 4.8 years, prepregnancy BMI 28.2 ± 5.2 kg/m2) were studied. Blood ketones were present in 37.6% of the cases before breakfast, 13.9% before lunch, and 11.9% before dinner. Women with at least one daily presence of blood ketones composed 40.6% of the sample. Presence of fasting blood ketones was correlated with ketone presence before lunch (r = 0.63, p < 0.0001) and before dinner (r = 0.55, p < 0.0001) and with mean glucose levels (r = 0.23, p = 0.02) 1 h after breakfast.
Blood ketone testing in women with gestational diabetes mellitus can detect a larger number of ketosis episodes than a urinary ketone test. Intensive blood ketone measurement should be recommended to women with gestational diabetes mellitus.
Reference:
Pintaudi, B., Giunta, L., Di Vieste, G. et al. Evaluation of ketone intensive measurement in women with gestational diabetes (EVOKING) study. Hormones (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-025-00663-1
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


