- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Diabetic Retinopathy Independently Predicts Higher Cardiovascular Mortality among diabetes patients, study finds
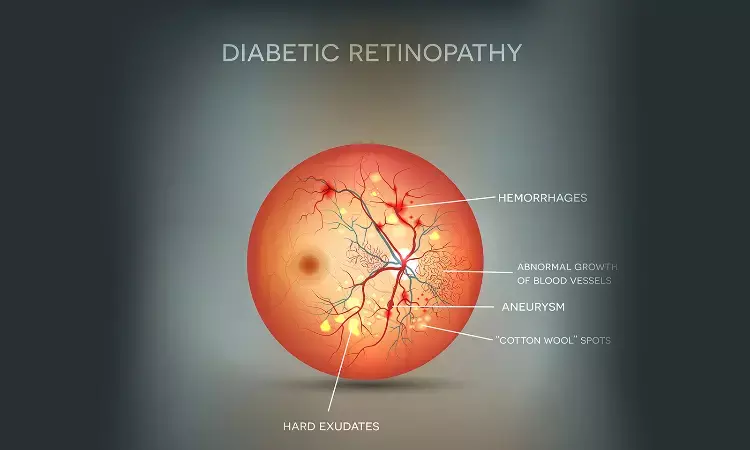
Researchers in a new study found that diabetic retinopathy (DR) is closely associated with an increased risk for myocardial infarction (MI) and cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality. This study conducted in acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients undergoing coronary angiography investigated whether DR is a predictor for CVD mortality. The study was conducted by Richard Kha and fellow researchers published in the journal of Scientific Reports.
This prospective cohort study included 1582 adult patients undergoing evaluation for ACS at a tertiary hospital in Australia. All had coronary angiography performed in order to assess for coronary artery disease and had concurrent fundus photography performed in order to assess for DR. On the basis of the International Clinical Classification of DR, DR was graded from none through to mild, moderate-to-severe NPDR, to proliferative. CAD severity was measured with the Gensini score. After 9 years of follow-up, CVD mortality was ascertained by data linkage with the Australian National Death Index. Statistical analyses were done to test the association of DR with CVD mortality after adjusting for age, sex, diabetes, cholesterols, smoking, hypertensive therapy, any prior myocardial infarction, or stroke.
Key Results
• At baseline, DR was found in 355 participants (22.4%).
• CVD death occurred in 181 cases over a follow-up period of 9 years (11.4%).
• Overall relative risks were also found to be 1.8 times greater for individuals with DR, compared to those without it (HR: 1.84, 95% CI: 1.30-2.61).
• Moderate NPDR significantly contributed to death from CVD at an elevated risk of 85% (HR: 1.85, 95% CI: 1.26-2.72).
• In this case, proliferative DR, contrary to the above, had the highest rise in risk, with the CVD mortality HR reaching 5.27 (95% CI: 2.32-12.00).
• These correlations remained significant after adjustments were made for the severity of coronary artery disease, based on two models, wherein cases without diabetes were omitted from the analysis.
• In both men (HR: 2.25, 95% CI: 1.60-3.19) and women (HR: 2.38, 95% CI: 1.24-4.58) with DR, the risk for CVD was significantly elevated.
The study authors concluded an independent association between DR and increased CVD mortality among a cohort of high-risk individuals. DR evaluation should be part of the cardiovascular risk stratification model undertaken by clinicians. DR patients should always be put under special surveillance and monitoring to evade fatality from CVD events and assure long-term survival outcomes.
Reference:
Dr Riya Dave has completed dentistry from Gujarat University in 2022. She is a dentist and accomplished medical and scientific writer known for her commitment to bridging the gap between clinical expertise and accessible healthcare information. She has been actively involved in writing blogs related to health and wellness.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


