- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Digital diabetes intervention effective in improving blood sugar levels, diabetes: Study
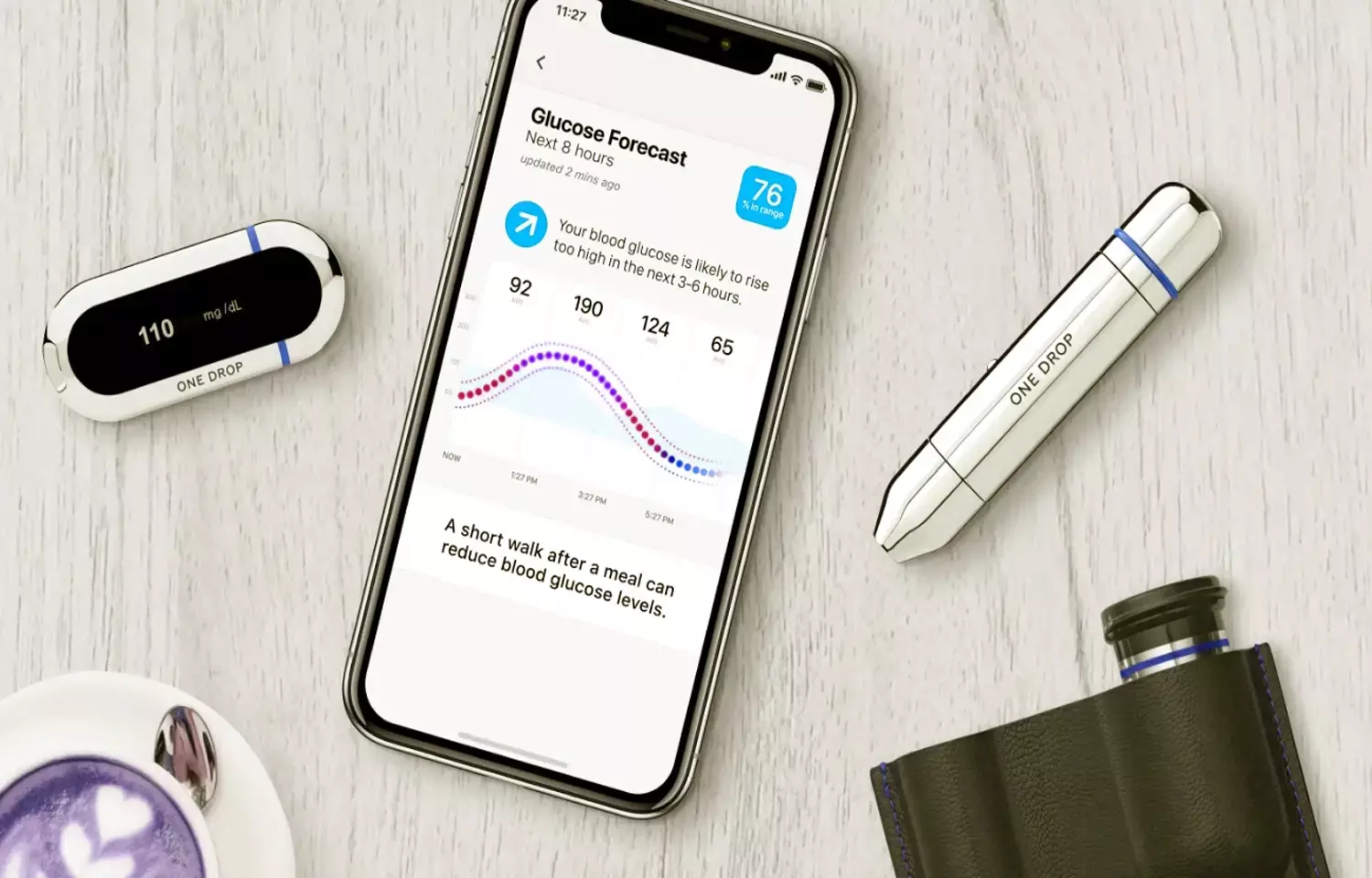
USA: Type 2 diabetes patients enrolled in a digital diabetes management intervention experienced clinically relevant meaningful improvements in blood sugar control, according to a recent study in JMIR Diabetes.
The findings suggest that a digital health intervention may be an effective, scalable, and accessible solution to diabetes management and improved blood sugar.
Traditional lifestyle interventions have shown limited success in improving diabetes-related outcomes. Digital interventions with continuously available support and personalized educational content may offer unique advantages for self-management and glycemic control.
Diabetes control is a major challenge faced by diabetes patients. It is a disease that requires daily attention to and navigation of myriad decisions—choosing foods, taking medication, monitoring blood glucose, and accessing preventive and acute care.
Traditional interventions have not shown to be very effective in improving diabetes-related outcomes. Digital interventions with continuously available support and personalized educational content may offer unique advantages for self-management and glycemic control. Considering this, Gretchen Zimmermann, Vida Health, San Francisco, CA, US, and colleagues aimed to evaluate changes in glycemic control among participants with type 2 diabetes who enrolled in a digital diabetes management program.
The study employed a single-arm, retrospective design. A total of 950 participants with a hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) baseline value of at least 7.0% enrolled in the Vida Health Diabetes Management Program. The intervention included one-to-one remote sessions with a Vida provider and structured lessons and tools related to diabetes management.
HbA1c was the primary outcome measure. Of the 950 participants, 258 (27.2%) had a follow-up HbA1c completed at least 90 days from program start.
Key findings of the study include:
· The researchers observed a significant reduction in HbA1c of –0.81 points between baseline (mean 8.68, SD 1.7) and follow-up (mean 7.88, SD 1.46).
· Among participants considered high risk (baseline HbA1c≥8), there was an average reduction of –1.44 points between baseline (mean 9.73, SD 1.68) and follow-up (mean 8.29, SD 1.64).
· Average follow-up HbA1c (mean 7.82, SD 1.41) was significantly lower than pre-enrollment HbA1c (mean 8.12, SD 1.46) There was also significant effect of program usage on HbA1c change (β=–.60) such that high usage was associated with a greater decrease in HbA1c (mean –1.02, SD 1.60) compared to low usage (mean –.61, SD 1.72).
"The present study revealed clinically meaningful improvements in glycemic control among participants enrolled in a digital diabetes management intervention. Higher program usage was associated with greater improvements in HbA1c," wrote the authors.
"The findings of the present study suggest that a digital health intervention may represent an accessible, scalable, and effective solution to diabetes management and improved HbA1c. The study was limited by a nonrandomized, observational design and limited postenrollment follow-up data," they concluded.
Reference:
The study titled, "Improved Glycemic Control With a Digital Health Intervention in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes: Retrospective Study," is published in the journal JMIR Diabetes.
DOI: https://diabetes.jmir.org/2021/2/e28033/
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


