- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Electrical stimulation improves glucose tolerance in obese individuals: Study
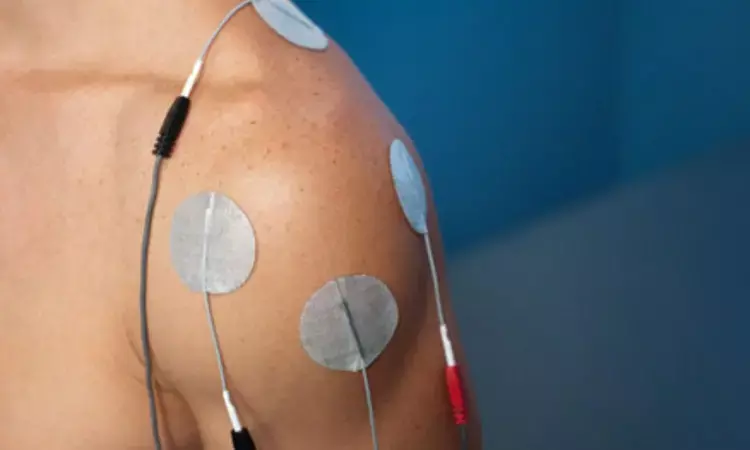
Australia: Michelle J Galvan and the team in a recent study showed neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) to be a novel and effective strategy for improving glucose tolerance in the overweight or obese sedentary population who are at risk. The study appears in the journal Endocrine Connections.
Exercise is a highly effective intervention in improving metabolic health and insulin sensitivity. American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) has set some minimum exercise criteria in its recommendations, and most US adults (54%) do not meet these requirements. NMES is a novel alternate strategy for inducing muscle contraction. However, there is no clarity on the effectiveness of NMES to improve energy expenditure and insulin sensitivity. Dr. Galvan and colleagues, therefore, aimed to examine the effects of four weeks of NMES on glucose tolerance in sedentary overweight or obese population.
The study included 10 participants aged: 36.8 ± 3.8 years, and having a BMI=32 ± 1.3 kg/ m2. They were randomized into either control or NMES groups. All participants received bilateral quadriceps stimulation (12 sessions; 30 minutes/session; 3 times/week at 50 Hz and 300 μs pulse width) altering pulse amplitude to either provide low-intensity sensory level (control; tingling sensation) or at high-intensity neuromuscular level (NMES; maximum tolerable levels with visible muscle contraction).
A three-hour oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) was used to assess glucose tolerance. Substrate utilization was measured by indirect calorimetry and body composition via dual X-ray absorptiometry at baseline and after four weeks of NMES intervention.
Following were the study's key findings:
- Control and NMES groups had comparable fasting blood glucose, glucose tolerance, substrate utilization, and muscle mass at baseline.
- Four weeks of NMES resulted in a significant improvement in glucose tolerance measured by OGTT, whereas no change was observed in the control group.
- There was no change in substrate utilization and in muscle mass in both control and NMES groups.
To conclude, four weeks of NMES (12 sessions) was shown to improve glucose tolerance in sedentary overweight or obese population.
The researchers however note the need for future studies to determine whether the NMES induced improvement in glucose tolerance offers a novel and effective strategy to improve long-term energy expenditure, insulin sensitivity, and body composition in an at-risk overweight or obese Hispanic population.
Reference:
Galvan, M. J., Sanchez, M. J., McAinch, A. J., Covington, J. D., Boyle, J. B., & Bajpeyi, S. (2022). Four weeks of electrical stimulation improves glucose tolerance in sedentary overweight or obese Hispanic population, Endocrine Connections (published online ahead of print 2022), EC-21-0533. Retrieved Jan 15, 2022, from https://ec.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/ec/aop/ec-21-0533/ec-21-0533.xml
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


