- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Erythrocyte aggregation in diabetes patients with hyper cholesterol increases microvascular complications: Study
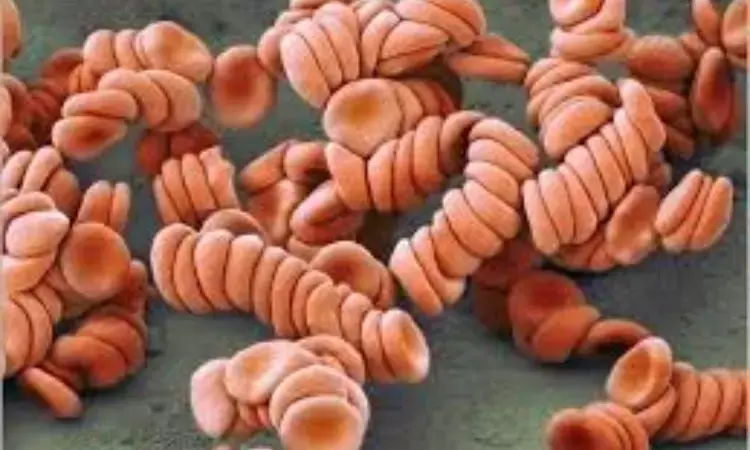
Tamil Nadu: A recent study in the journal Thrombosis Update found that in type 2 diabetes with hyper cholesterol, erythrocyte aggregation may increase the microcirculatory complications versus diabetes with normal cholesterol.
Many studies have been done on the aggregation of erythrocytes in many pathological conditions like malaria, diabetes mellitus, hyper cholesterol, jaundice, etc. Different types of erythrocyte aggregation occur in different pathological conditions. Increased aggregation was found in pathological conditions versus control subjects.
Against the above background, N.Babu, Vinayaka Missions Kirupanantha Variyar Engineering College, Vinayaka Missions Research Foundation, Salem, Tamil Nadu, India, aimed to study the aggregation of erythrocytes in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients without cholesterol and with cholesterol and to compare such subjects with healthy subjects.
For this purpose, the researchers determined aggregation of erythrocytes using an online erythrocyte aggregometer based on sequential analysis of transmitted laser light intensity after passing through the erythrocyte suspension in plasma. The aggregation mechanism was determined in terms of various aggregation parameters such as aggregation sedimentation time index (ASTI), aggregation size index (ASI), and the total number of fluctuations (TNF) of erythrocyte aggregates. The dynamic nature of the aggregation process under gravitation quantitatively was described using these parameters
There were a total of 45 subjects (control subjects (n = 10)), diabetes with normal cholesterol (n = 24), and diabetes with hyper cholesterol (n = 21) in this study.
Salient findings of the study include:
- The aggregation parameter total number of fluctuations (TNF) was 1634 ± 397 in normal subjects, 1539 ± 197 in group 1, and 1096 ± 180 in group 2.
- The aggregation sedimentation time index (ASTI, Fig. 2) indicates the time taken by the aggregates to sediment (28–32 min for normal, 24–28 min for group 1, and 16–20 min for group 2 subjects).
- The aggregation parameters decreased in diabetes with normal cholesterol and were significantly decreased in diabetes with hyper cholesterol compared to controls.
- The results show that in patients with diabetes with normal cholesterol, the aggregation of erythrocytes is increased and in patients with diabetes with hyper cholesterol, the aggregation increased significantly.
To conclude, the significant increase in aggregation in diabetes with hypercholesterol may increase the microcirculatory complications versus diabetes with normal cholesterol.
Reference:
The study titled, "Hemorheological study on erythrocyte aggregation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus without cholesterol and with hyper cholesterol," was published in the journal Thrombosis Update.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


