- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Flash glucose monitoring effective strategy for monitoring blood sugar in diabetes patients, study suggests
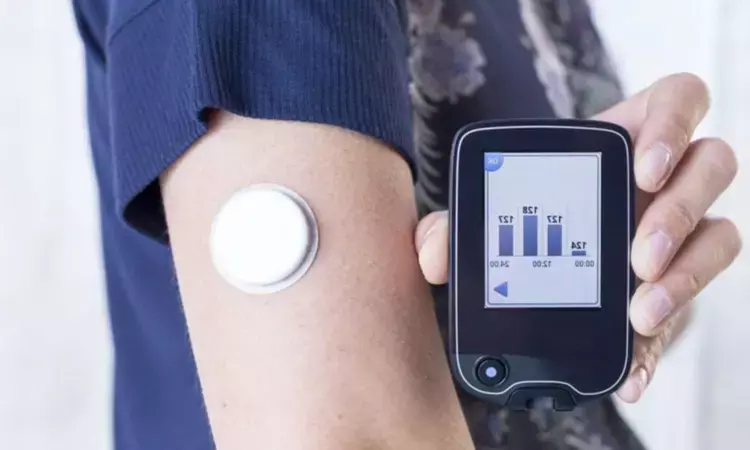
China: Flash glucose monitoring (FGM) is an effective strategy for keeping track of blood sugar levels in diabetes patients, a recent study in the Journal of Diabetes and its Complications has revealed.
The study showed that flash glucose monitoring is better than self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) in improving glycated hemoglobin levels, fasting plasma glucose levels, and 2-h postprandial glucose level; and decreases the number of hypoglycemic events.
FGM was introduced in the international market in 2014; since its introduction, academics globally are exploring its relevance for improving glycemic control in diabetics. It uses a sensor placed on the back of the upper arm, and the user wears it externally; this allows monitoring of glucose information through a mobile app.
Min Zhou, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Jiangxi, China, and colleagues conducted the study to examine the effect of FGM on glycemic control among patients with diabetes mellitus.
For this purpose, the researchers searched online databases to collect randomized controlled trials (RCTs) related to the effect of FGM on blood sugar control in diabetes patients. Outcomes were hypoglycemic events, glycated hemoglobin, 2-h postprandial glucose (2hPG) levels, and fasting plasma glucose (FPG).
A total of 19 studies of 2013 participants were included, all of which were randomized controlled trials.
The study led to the following findings:
- Meta-analysis results revealed that FGM compared to self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG), significantly reduced glycated hemoglobin levels in type 2 diabetes patients [mean difference = −0.74] and type 1 diabetes mellitus combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus [mean difference = −1.14], with a more significant effect in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients aged ≤65 years with (mean difference = −1.38).
- No effect of FGM was observed on the improvement of glycated hemoglobin levels in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
- 2-h postprandial glucose levels and fasting plasma glucose levels were remarkably lower in FGM than in SMBG, and the number of hypoglycemic events was considerably lower.
The findings suggest FGM is an effective strategy for monitoring glucose levels in patients with diabetes mellitus. FGM to improve glycated hemoglobin levels was more effective in patients with type 2 diabetes ≤65 years of age. Also, FGM use reduced the number of hypoglycemic events.
"Comparing SMBG with FGM suggests that FGM improves 2-h postprandial glucose levels, fasting plasma glucose levels, and glycated hemoglobin levels, and reduces the number of hypoglycemic events," the researchers wrote in their conclusion.
Reference:
Gao, Yuan, et al. "Effects of Flash Glucose Monitoring On Glycemic Control in Participants With Diabetes Mellitus: a Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials." Journal of Diabetes and Its Complications, vol. 36, no. 11, 2022, p. 108314.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


