- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Flash glucose monitoring improves glycemic control and treatment satisfaction in non-insulin treated diabetes patients
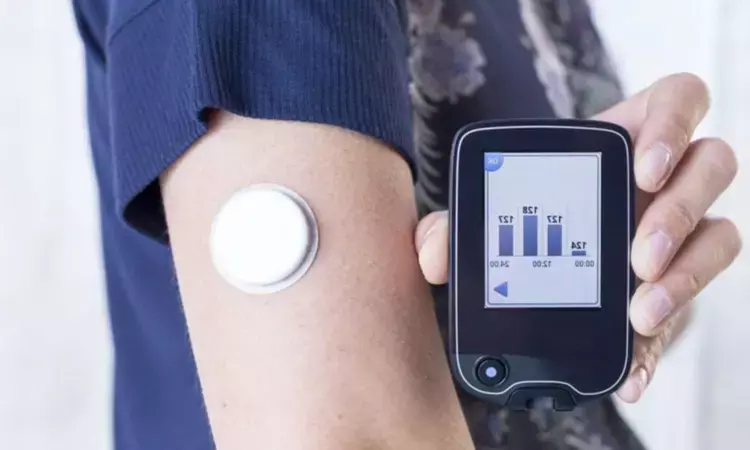
Japan: An analysis of a randomized controlled trial revealed improvement in blood sugar control soon after flash glucose monitoring (FGM) initiation, accompanied by improved satisfaction with the continuation of the current treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) not treated with insulin.
Flash glucose monitoring, also called intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring (isCGM), is a type of glucose monitoring device that can measure glucose levels in the subcutaneous interstitial fluid through a sensor worn on the patient's back of the upper arm. It allows patients to get their current glucose trends and a graph of the glucose reading over the preceding 8 hours, and they can understand their rise in glucose after a meal or lowering from a physical exercise. Such features may motivate them to follow exercise and diet therapy.
If FGM use is effective for diabetes self-management and lifestyle improvement, it can also be expected to be effective in noninsulin-treated T2D patients. Based on this hypothesis, Ayaka Hayase, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, Nagoya, Japan, and colleagues previously conducted an RCT analysing the effects of conventional self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) and FGM on glycemic control in these patients. They showed that FGM use improved glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) which was sustained after the cessation of glucose monitoring.
In the study, published in Primary Care Diabetes, the investigators analyzed the changes in various parameters with using FGM to clarify the factors that affect the improvement in glycemic control with FGM use. They used data from 48 of 49 participants with noninsulin-treated type 2 diabetes who were in the groups using FGM from the previous study.
The analysis led to the following findings:
- Analyses of the FGM data during the 12-week FGM provision period showed that the weekly mean blood glucose levels considerably decreased as early as 1 week compared with the baseline values, and this decline continued for 12 weeks.
- An enhancement in the Diabetes Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire regarding the "willingness to continue the current treatment" score was significantly associated with the improvement in HbA1c at 12 and 24 weeks.
- HbA1c improvement was associated with an improvement in treatment satisfaction.
- Changes in HbA1c were correlated with the percentage of time CGM is active.
"Rapid and prolonged improvement in HbA1c with the FGM use was associated with improved satisfaction with continuing the current treatment in patients with noninsulin-treated type 2 diabetes," the researchers concluded.
Limitations of the study were that the study used previous trial data and the number of participants was limited. Also, they did not assess lifestyle changes in the participants.
They suggested performing a prospective study using FGM as an empowerment tool for diabetes self-management in the future to evaluate lifestyle improvement by FGM use and to clarify effective support in conjunction with the use of FGM.
Reference:
Hayase, Ayaka, et al. "Improved Glycemic Control After the Use of Flash Glucose Monitoring Accompanied By Improved Treatment Satisfaction in Patients With Non-insulin-treated Type 2 Diabetes: a Post-hoc Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial." Primary Care Diabetes, 2023.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


