- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Frailty Significantly Increases Type 2 Diabetes Risk among those with genetic predisposition, UK Study Finds
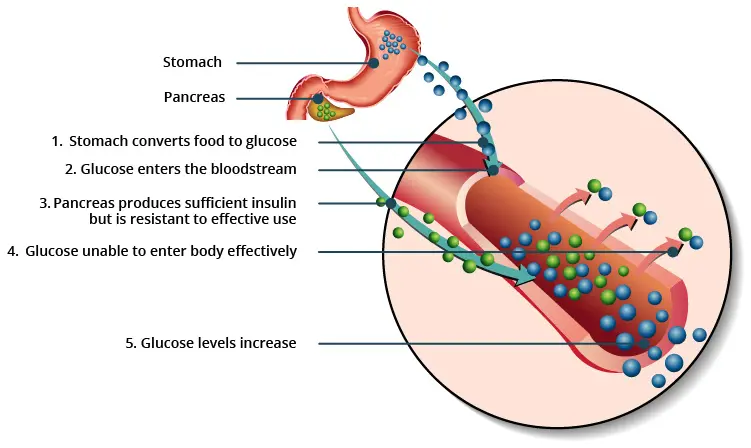
According to a large UK Biobank study published in Cardiovascular Diabetology, individuals with prefrailty or frailty have a notably higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, especially when coupled with high genetic susceptibility. Researchers identified a frailty-related metabolic signature that mediates up to one-third of this risk, underscoring the combined roles of biological aging, inflammation, and genetics in diabetes development.
Individuals with frailty are at increased risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D), but the underlying mechanisms are unclear. We aimed to investigate whether the frailty-T2D association is mediated by alterations in the metabolome and assess potential interaction with genetic susceptibility to diabetes.
This retrospective analysis, using data from a large prospective population-based cohort, included a total of 197,502 adults with baseline metabolomics data from the UK Biobank. Frailty was defined using the Fried frailty phenotype according to five components. Elastic net regression was applied to create a frailty-related metabolic signature.
We assessed hazard ratios (HR) and its 95% confidence interval (CI) of incident T2D in relation to the baseline metabolic signature of frailty and examined the mediating role of the metabolic signature in the effect of frailty on T2D. Additive interaction between the metabolic signature and polygenic risk score for T2D (PRS-T2D) on the incidence of T2D was assessed as relative excess risk due to interaction (RERI).
Results: Compared with non-frailty, the HR (95% CI) of incident T2D in pre-frailty and frailty was 1.33 (1.26, 1.40) and 1.59 (1.46, 1.74), respectively. The metabolic signature of frailty (comprised of 53 metabolites) was positively associated with T2D risk (HR per standard deviation increment: 1.45; 95% CI: 1.42, 1.48), and explained 31.0% (95% CI: 25.8, 36.8) of the association between frailty and T2D.
An additive interaction between metabolic signature of frailty and PRS-T2D was found (RERI: 9.43; 95% CI: 6.06, 12.80). The increased risk of T2D in individuals with frailty may be mediated through effects on the metabolome, and the influence of such metabolic alterations on diabetes risk may be amplified in individuals with genetic susceptibility to T2D.
Reference:
Wang, Y., Chen, S., Li, Y. et al. Metabolic profiling of frailty, associations with type 2 diabetes and interaction with genetic susceptibility. Cardiovasc Diabetol 24, 226 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-025-02776-8
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


