- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Gastric bypass best weight loss option for diabetes patients, study finds
NEW YORK, NY - Bariatric surgery-either gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy-is recommended for people with type 2 diabetes and a body mass index of 40 or above. But the optimal treatment remains unclear and may depend on the severity of the patient's diabetes.
Using data from previous studies and databases, researchers at Columbia University's Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, led by Chin Hur, MD, MPH, created a model to investigate the effectiveness, quality of life gains, costs, and complications of gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and medical therapy among patients over a five-year period.
The study is the first to consider diabetes severity in a comparison of gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy, which are the two most popular forms of bariatric surgery in the United States.
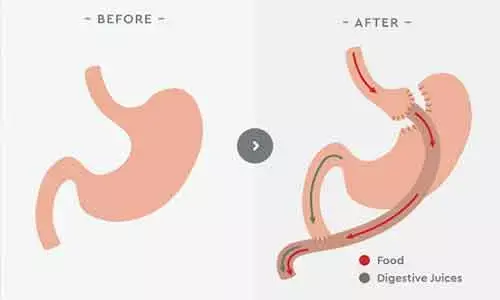
Gastric bypass is a more complex procedure than sleeve gastrectomy, and previous studies show it is associated with more complications. Gastric bypass creates a small pouch in the stomach that is attached to the small intestine, so that food bypasses much of the stomach and some of the small intestine. After the surgery, less food can be ingested and absorbed. In sleeve gastrectomy, the stomach is permanently reduced to about one quarter of its original size, but no bypass is created.
The new analysis projected that gastric bypass leads to greater weight loss and a greater rate of remission of diabetes than sleeve gastrectomy or medical therapy, which involves lifestyle counseling and medication.
Gastric bypass surgery also was projected to produce the best results regardless of diabetes severity.
"Determining which groups may benefit from a specific strategy is an important step toward personalized medicine," says Hur.
"Our study suggests that in most cases, gastric bypass is the preferred strategy when looking at a five-year time frame, despite higher upfront surgical costs and complications, and becomes even more cost-effective when considered over 10 or 30 years."
http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.48317
Hina Zahid Joined Medical Dialogue in 2017 with a passion to work as a Reporter. She coordinates with various national and international journals and association and covers all the stories related to Medical guidelines, Medical Journals, rare medical surgeries as well as all the updates in the medical field. Email: editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


