- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Graves' disease patients with thymic hyperplasia may exhibit higher serum calcium levels
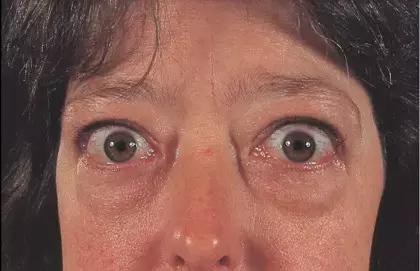
Graves'disease patients with thymic hyperplasia may exhibit higher serum calcium levels suggests a new study published in the BMC Endocrine Disorders.
Graves' disease increases bone resorption in hyperthyroidism, leading to elevated serum calcium levels and a negative bone balance. Thymic hyperplasia is observed in some Graves' disease patients. What's more, there have been a few reports of increased serum calcium and severe osteoporosis induced by Graves’ disease with thymic hyperplasia. It remains unclear whether Graves’ disease with thymic hyperplasia is associated with higher serum calcium levels. Our study aimed to investigate the possibility of elevated serum calcium levels and aggravated bone mobilization in Graves’ disease patients with thymic hyperplasia. Newly diagnosed and untreated patients with Graves' disease (n = 96) were enrolled. They were divided into two groups based on the incidental detection of thymic hyperplasia during imaging. Albumin, alkaline phosphatase, calcium, free triiodothyronine, free thyroxine, thyroid-stimulating hormone, and thyrotrophin receptor antibody (TRAb) were measured, and a computerized tomography of the chest was obtained.
Results: Patients with Graves’ disease who had thymic hyperplasia were notably younger (P=0.018) and exhibited higher serum calcium levels (P=0.001) compared to those with Graves’ disease without thymic hyperplasia. In the multiple regression analysis, thymic hyperplasia, TRAb, and female gender were significant variables associated with elevated serum calcium levels in patients with Graves' disease, collectively accounting for 31.7% of the variation in serum calcium. Graves’ disease patients with thymic hyperplasia showed higher serum calcium levels. thymic hyperplasia, TRAb, and female gender were found to be correlated with increased serum calcium levels in Graves’ disease, suggesting a potential association between thymic hyperplasia and bone mobilization in Graves’ disease.
Zeng, J., Li, L. & Wei, D. Association between thymic hyperplasia and serum calcium level in Graves’ disease. BMC Endocr Disord 24, 15 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-024-01541-4
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


