- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
HIV Drug Lamivudine Shows Early Vision Improvement in Diabetic Macular Edema: Study
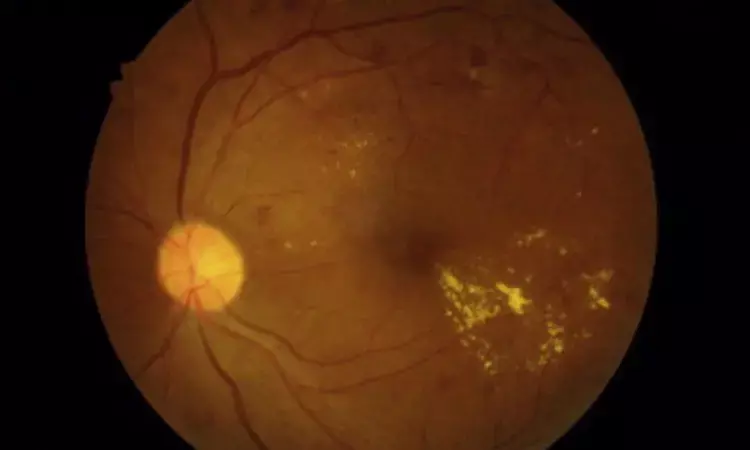
A study published in Med has found that the HIV medication lamivudine significantly improved visual acuity in adults with diabetic macular edema by week 4, compared to a placebo. This finding may revolutionize treatment protocols for one of the most common causes of vision impairment in individuals with diabetes. The conventional treatment for DME is monthly intraocular injections of costly anti-VEGF drugs like bevacizumab, aflibercept, or ranibizumab. The study was conducted by Felipe P. and colleagues.
Diabetic macular edema is a disease affecting millions of people globally, resulting from chronic inflammation and fluid accumulation within the macula. While anti-VEGF injections are the treatment of choice at present, they are often associated with pain, burden to the patient, and cost. Lamivudine, an oral drug originally approved for HIV and hepatitis B, was repurposed in DME because it acts on inflammasomes, providing a non-surgical path for treatment. This first-in-human clinical trial was registered on the Brazilian Registry of Clinical Trials (RBR-87b6r5s) and carried out between February 2022 and September 2023.
The study included 24 adult subjects with one or both eyes with center-involved DME and a best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) of less than 69 letters. Subjects were randomized 1:1 into two groups: 10 patients (16 eyes) were treated with lamivudine (150 mg twice a week), and 14 patients (21 eyes) were treated with a placebo. At week 4, all patients received an intravitreous bevacizumab injection (1.25 mg). Co-primary outcome was changed in BCVA at weeks 4 and 8. Comparisons were to synthetic controls from the DRCR.net Protocol T database. Secondary outcomes were alterations in retinal thickness and adverse event incidence.
Key Findings
• The lamivudine group, at 4 weeks, had an improvement of 9.8 letters in BCVA, whereas the placebo group had a decrease in BCVA by 1.8 letters (p < 0.001).
• At 8 weeks, the lamivudine plus bevacizumab group had a gain of 16.9 letters in BCVA, compared with a 5.3-letter increase in the placebo plus bevacizumab group (p < 0.001).
• Lamivudine had more visual gain compared to bevacizumab and ranibizumab (p < 0.05), and its efficacy was on par with aflibercept (p = 0.5).
• There were no significant retinal thickness differences between groups.
• The intervention was well tolerated, and there were no significant differences in adverse events between groups.
This groundbreaking study demonstrates a stunning improvement in visual acuity in patients with DME involving the center of the macula with oral lamivudine, and further augmented with the effect when administered in combination with bevacizumab injections. Given its affordability, oral formulation, and promising efficacy, lamivudine can potentially transform the global treatment scenario of DME by providing a cheaper, less invasive alternative to millions of patients globally.
Reference:
Dr Riya Dave has completed dentistry from Gujarat University in 2022. She is a dentist and accomplished medical and scientific writer known for her commitment to bridging the gap between clinical expertise and accessible healthcare information. She has been actively involved in writing blogs related to health and wellness.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


