- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Older, White Male Smokers at Higher Risk for Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Study
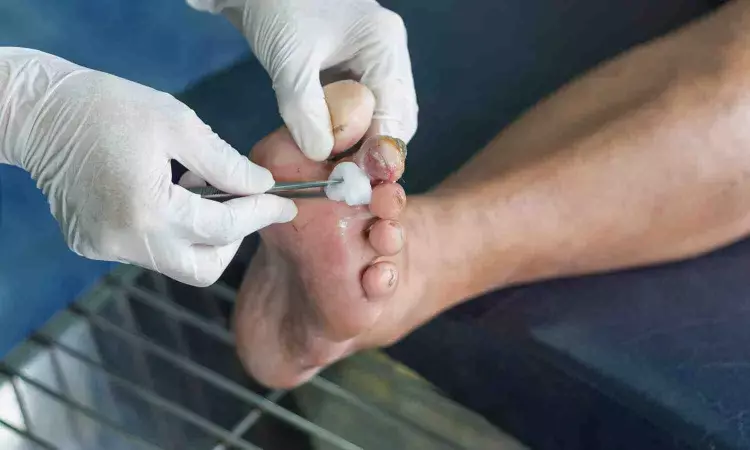
Researchers have identified that some subgroups of patients with diabetes, older males, smokers, and White ethnicity, are at significantly increased risk of developing diabetic foot ulcer disease (DFUD), a severe condition with a poorer five-year survival rate than most cancers. The study was published in Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism by Safoora G. and colleagues. The research found that those with higher systolic blood pressure and a higher baseline HbA1c level were more likely to develop DFUD.
DFUD is a long-standing, life-changing diabetic complication that is frequently under-diagnosed with regard to its catastrophizing effects. Previously, almost all risk factor information was derived from small, clinic-based surveys that tended to be cross-sectional in design. The current study sought to address the deficit through the utilization of two large and independent English and Scottish diabetic cohorts, providing one of the largest analyses to date.
The research evaluated a combined total of 391,790 individuals with diabetes—131,042 from England via the Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD), and 260,748 from Scotland via the Scottish Diabetes Research Network-National Diabetes Dataset (SDRN-NDS). The English cohort included primary and secondary care data, whereas the Scottish cohort utilized secondary care and foot clinic data.
Key Findings
Incidence of DFUD:
• In the English cohort, 4.7% of patients developed DFUD during a median follow-up of 4.3 years, representing an incidence rate of 9.0 per 1,000 person-years (95% CI: 8.8–9.2).
• In the Scottish cohort, 2.9% of patients developed DFUD during a median follow-up of 6.3 years, with an incidence rate of 4.4 per 1,000 person-years (95% CI: 4.3–4.5).
Common Risk Factors Identified in Both Populations:
• Age: The older patients had higher chances of developing DFUD.
• Sex: Males were more vulnerable.
• Ethnicity: Individuals of White ethnicity were having greater incidence rates.
• Lifestyle: Smokers were much more likely to develop DFUD.
• Clinical indicators: Greater systolic blood pressure and baseline HbA1c levels were strongly related with subsequent DFUD.
This study provides strong evidence to support the targeting of these high-risk groups in diabetes care programs. These findings can provide the impetus for more effective prevention strategies, lowering the life-changing costs of diabetic foot ulcer disease.
Reference:
Gharibzadeh S, Lee J, Highton P, Greenlaw N, Gillies C, Zaccardi F, Brennan A, Pollard DJ, Valabhji J, Game F, Stanley B, Leese G, Gray L, Tesfaye S, Webb D, Wild S, Shabnam S, Davies M, Khunti K, Petrie J, Gregg E. Risk factors for development of diabetic foot ulcer disease in two large contemporary UK cohorts. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 Jun 24. doi: 10.1111/dom.16519. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40555701.
Dr Riya Dave has completed dentistry from Gujarat University in 2022. She is a dentist and accomplished medical and scientific writer known for her commitment to bridging the gap between clinical expertise and accessible healthcare information. She has been actively involved in writing blogs related to health and wellness.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


