- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Postural Variation In DLCO Identifies Pulmonary Microangiopathy in T2DM patients
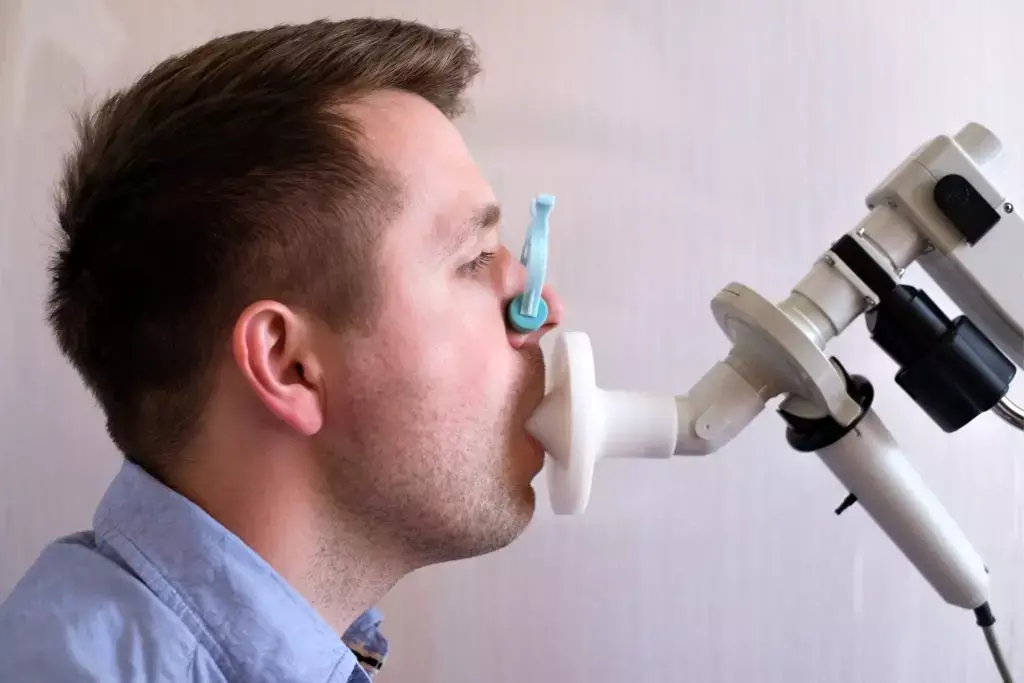
Diabetes-related microvascular and macrovascular complications cause a significant increase in morbidity and mortality.
A recent study suggests that postural variation in Diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) is a useful test in identifying pulmonary microangiopathy among patients with Type II diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The study findings were published in the Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews on December 15, 2021.
Lower Forced Vital capacity (FVC), Forced Expiratory Volume in the first second (FEV1) & DLCO occurs in adults with T2DM compared to non-diabetic individuals. Reduction in lung function correlates with glycemic status and duration of diabetes independent of smoking or obesity. Still, the entity of pulmonary microangiopathy is often under-recognized clinically and its awareness among general practitioners managing diabetes remains low likely due to its subclinical lung function abnormalities. Therefore, Dr Arun K and his team conducted a study assessing the occurrence of pulmonary microangiopathy among T2DM using dynamic DLCO.
In an observational study, the researchers included 120 participants and divided them into 3 groups. Group 1 comprised T2DM with microangiopathy (n = 40), group 2 include T2DM without microangiopathy (n = 40), group 3 were healthy controls (n = 40). Using electronic spirometry, they measured the FEV1, FVC and calculated the FEV1/FVC ratio. They measured the DLCO (%predicted) using the single breath method in the sitting position followed by the supine position and calculated delta DLCO. They further compared the measured DLCO between the three groups.
Key findings of the study:
- Upon analysis, the researchers found that DLCO (median [IQR]) in sitting (78 [70–82.75]) and supine position (70 [62–84]) among group one was significantly decreased when compared to the other two groups.
- They also found that delta DLCO (median, [IQR]) among patients with diabetic microangiopathy (−6 [-8 to −2]) was significant in comparison with group two (4[2,6]) and control group (5[4,6]).
- They noted that the negative delta DLCO reflecting pulmonary microangiopathy was significantly associated with extrapulmonary microangiopathy.
The authors concluded, "Postural variation in DLCO is a useful non-invasive test for identifying pulmonary microangiopathy among T2DM patients. Presence of pulmonary microangiopathy has a significant association with diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy."
For further information:
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


