- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Psoriasis patients have increased risk of diabetes development: BMC Study
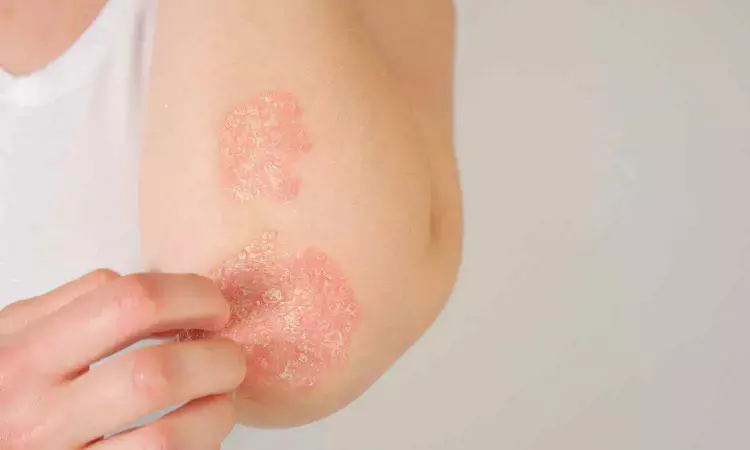
A recent study published in the Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome journal found those that psoriasis patients have a 48% higher chance of getting diabetes. Nearly 23% of the link between psoriasis and diabetes was found to be caused by obesity, making it a significant mediator.
Diabetes is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by high blood glucose levels and is a growing global health and financial burden, affecting nearly 10% of the population. Psoriasis which affects 2-4% of people is linked to depression, cardiovascular disease, oral health issues, and kidney disease. Obesity, another rising public health concern, increases the risk of diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. While obesity is a known risk factor for diabetes, the link between psoriasis and diabetes remains unclear. This study explored their relationship and assessed whether obesity serves as a mediator.
Data from a total of 21,835 NHANES participants between 2003–2006 to 2009–2014 were included in the study. Body mass index (BMI) and data on diabetes and psoriasis from questionnaires were included in the analysis. Weighted logistic regression was used in the study to investigate the relationship between diabetes and psoriasis.
Smooth curve fitting, stratified by age and gender, was used to investigate the nonlinear association between psoriasis, diabetes, and obesity. Furthermore, the mediation study revealed that the relationship between the prevalence of diabetes and psoriasis was partially mediated by fat.
The study discovered that people with psoriasis had a considerably greater incidence of diabetes after controlling for pertinent covariates. Diabetes incidence and BMI levels were found to be positively correlated in psoriasis patients, with a significant difference between the highest (Q4) and lowest (Q1) BMI quartiles.
The persistent correlation between BMI and diabetes, which was also visible in psoriasis patients, was further examined using smooth curve fitting. According to an age-stratified analysis, older adults with diabetes had a higher prevalence than younger people with the same BMI. In men, psoriasis was found to have an inflection point when BMI surpassed a particular threshold, at which point its prevalence started to decrease.
The prevalence of psoriasis also declined in younger persons over a certain BMI threshold. Also, psoriasis and diabetes were partially linked by obesity, which accounted for about 22.91% of this connection, according to mediation analysis. Overall, this study suggests a possible connection between diabetes and psoriasis, with fat perhaps acting as a mediating factor.
Reference:
Xu, Z., Ma, K., Zhai, Y., Wang, J., & Li, Y. (2025). Obesity mediates the association between psoriasis and diabetes incidence: a population-based study. Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome, 17(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-025-01622-x
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


