- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Tools to decrease hypoglycemia may improve sleep quality in young diabetics: Study
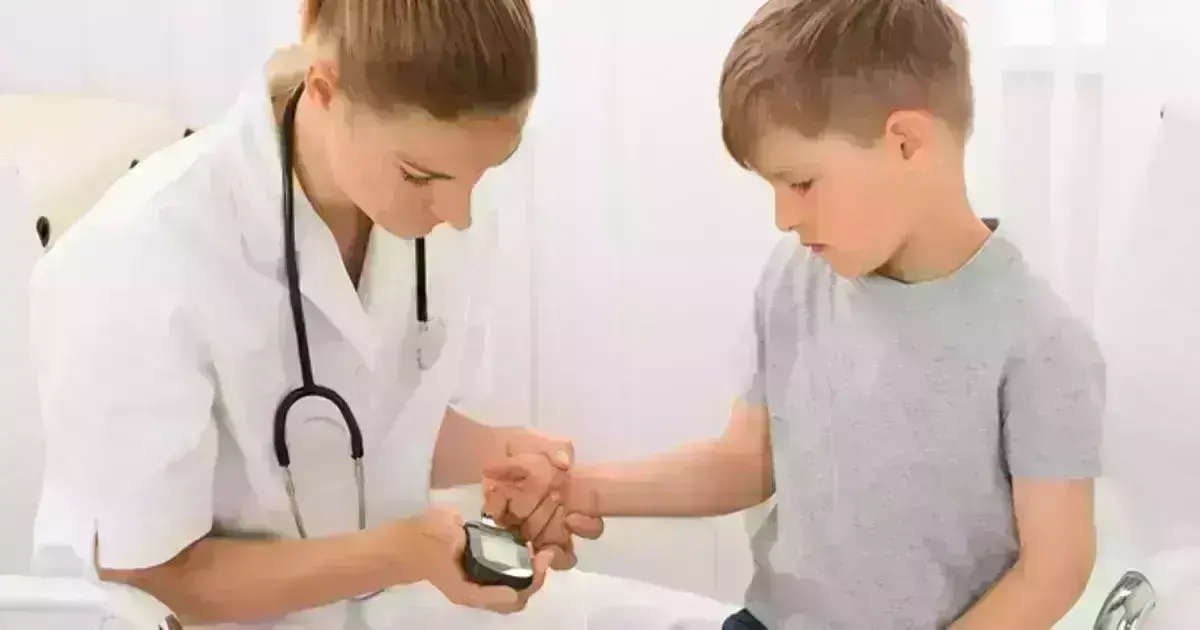
Improved hypoglycemia can be linked to quality sleep in the youth suffering from Type-1 diabetes, suggests a study published in the Diabetes journal and presented at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 81st Scientific Session.
Quality sleep is important for youth with type 1 diabetes (T1D) and their parents, yet disrupted sleep due to diabetes-related awakenings is common.
Diabetes-related sleep disturbance is a common event in the youth suffering from Type-1 diabetes as well as their parents. To achieve quality sleep, increased time-in-range (TIR, 70-180 mg/dL) and decreased time in hypoglycemia (<70 mg/dL) may be beneficial.
A study was conducted by a group of U.S.A researchers to assess the linkages between pediatric blood sugar levels and quality sleep measures.
The researchers conducted an observational study, wherein they selected a total of 26 children belonging to the age group of 3-17 years and their one parent each. All the participants had their sleep and glycemia data collected. Time-in-range and the duration of hypoglycemia were observed for an entire day, and the data obtained were compared with total sleep time (TST), sleep efficiency, wake-time after sleep onset (WASO), and several awakenings. They utilized 'Linear mixed models' to evaluate the associations between the sleep variables with Time-in-range and hypoglycemia.
The findings were as follows:
- Hypoglycemia was significantly associated with the youth's wake-time after sleep onset, awakenings, and total sleep time.
- Time-in-range was not significantly associated with sleep measures.
- Lastly, time in hypoglycemia was linked strongly with more nocturnal awakenings and wake-time after sleep onset in children with Type-1 diabetes.
The authors concluded that tools to decrease hypoglycemia can be crucial to improve sleep quality for youth with Type-1 diabetes. However, an association between hypoglycemia and a child's total sleep time established by this study remains an unexpected finding and will require further probing. Additionally, bigger sample size will be required to definitely affirm the associations between glycemic outcomes and quality sleep measures.
Reference:
A study titled,"157-LB: Association of Glycemic Ranges and Sleep Measures in Youth with T1D and Their Parents" by Karami A et. al presented at American Diabetes Association (ADA) 81st Scientific Sessions.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


