- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Use of CGM in type 1 diabetes patients may lower odds of developing retinopathy: Study
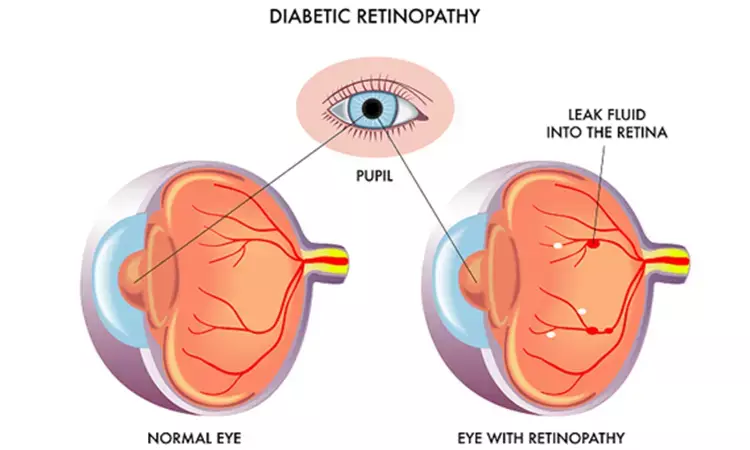
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a serious complication of type 1 diabetes (T1D) that can lead to vision impairment or blindness if left untreated. Understanding the impact of diabetes management technologies, such as continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and insulin pumps, on DR outcomes is crucial for improving patient care and outcomes. The use of CGM and insulin pumps has revolutionized diabetes management by providing real-time glucose data and precise insulin delivery.
A recent retrospective cohort study aimed to evaluate the association between CGM, insulin pump use, or both, and the development of DR and proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) in adults with T1D. This study was published in JAMA Network Open by T. Y. Alvin and colleagues.
The study included 550 adults with T1D from a tertiary diabetes center and ophthalmology center. Data were analyzed retrospectively from 2013 to 2021. Participants were categorized based on their use of diabetes technologies, including CGM, insulin pump, or both.
Key Findings:
• 62.7% of patients used CGM, 58.2% used an insulin pump, and 47.5% used both.
• 44% of participants had DR at any point during the study.
• CGM use was associated with lower odds of developing DR and PDR.
• In the longitudinal analysis, 21.8% of patients experienced progression of DR during the study period.
The study suggests that CGM use is associated with a reduced risk of developing DR and PDR in adults with T1D, even after adjusting for other factors like hemoglobin A1c levels. These findings underscore the potential benefits of CGM in diabetes management for mitigating the risk of DR and PDR. Early adoption and utilization of CGM technology may play a crucial role in preventing diabetic eye complications and improving long-term visual outcomes in individuals with T1D.
Reference:
Liu, T. Y. A., Shpigel, J., Khan, F., Smith, K., Prichett, L., Channa, R., Kanbour, S., Jones, M., Abusamaan, M. S., Sidhaye, A., Mathioudakis, N., & Wolf, R. M. Use of diabetes technologies and retinopathy in adults with type 1 diabetes. JAMA Network Open,2024;7(3):e240728. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.0728
Dr Riya Dave has completed dentistry from Gujarat University in 2022. She is a dentist and accomplished medical and scientific writer known for her commitment to bridging the gap between clinical expertise and accessible healthcare information. She has been actively involved in writing blogs related to health and wellness.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


