- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Button battery impaction causes severe pediatric airway injuries: JAMA
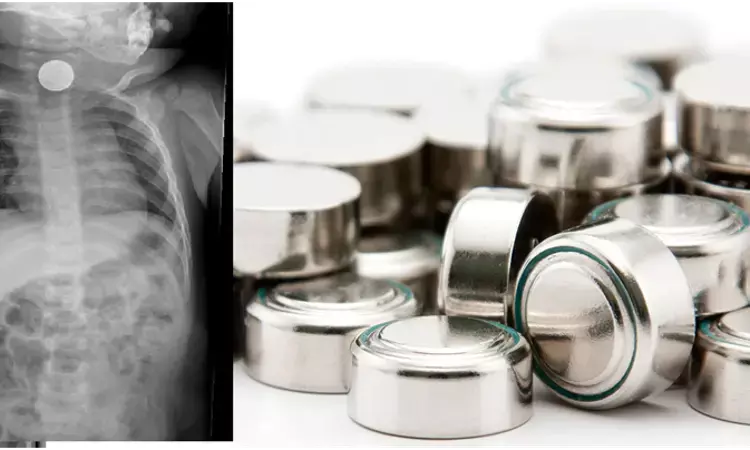
CANADA: Button battery ingestion causes severe airway injuries, mainly tracheoesophageal fistulae and vocal fold paralysis in younger children, a study published in JAMA Otolaryngology Head Neck Surgery. Timely BB removal (often tracheostomy) decreases the devastating consequences of these injuries.
The past few decades have seen an increase in morbidity and mortality due to BB ingestion. Many major complications present weeks to months after BB removal. Button batteries (BBs) are commonly found in many households. It causes severe injury to children if ingested. The direct opposition of the trachea and recurrent laryngeal nerves with the esophagus and liquefactive necrotic effects of BB impactions puts children at risk of serious airway injury.
The present study was conducted by Justine Philteos, Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Toronto, and the team to analyze airway injuries after BB ingestion, to raise awareness, highlight management strategies, and develop protocols for prevention.
For this systematic review, a comprehensive strategy was designed to search MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Web of Science, and CINAHL (Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature) from inception to July 31, 2021. Additional cases were identified from the National Capital Poison Center BB registry and individual authors also gave additional information.
The study included a total of 195 patients who developed airway injuries after BB ingestion in the analysis. The mean (SD) age at BB ingestion was 17.8 (10.2) months and the mean (SD) time from BB ingestion to removal was 5.8 (9.0) days.
Key findings of the study
• The most common airway sequelae observed in the series were 155 tracheoesophageal fistulae and 16 unilateral vocal cord paralysis.
• Twenty-three children had bilateral vocal cord paralysis. The mean (SD) duration of ingestion leading to vocal cord paralysis was shorter than that of the general cohort.
• Children presenting with airway symptoms were likely to have a subsequent tracheoesophageal fistula or vocal cord paralysis.
• There were 14 deaths from BB ingestion. The mean (SD) age at BB ingestion was 11.8 (11) months, which was not different from that of the general cohort.
The authors finally concluded that airway injuries are a severe consequence of BB ingestion. Otolaryngologic follow-up is a must for these children as vocal cord injuries can occur even if exposure is of very short duration. Preventive strategies, such as educating parents, safer battery designs, safe disposal of BBs, and safer manufacturing standards for BBs can mitigate BB ingestion and sequelae.
Reference:
Philteos J, James AL, Propst EJ, et al. Airway Complications Resulting From Pediatric Esophageal Button Battery Impaction: A Systematic Review. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. Published online May 26, 2022. doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2022.0848
BDS
Dr. Hiral patel (BDS) has completed BDS from Gujarat University, Baroda. She has worked in private dental steup for 8years and is currently a consulting general dentist in mumbai. She has recently completed her advanced PG diploma in clinical research and pharmacovigilance. She is passionate about writing and loves to read, analyses and write informative medical content for readers. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


