- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Coblation cryptolysis safe, effective for treatment of tonsil caseum-induced halitosis: Study
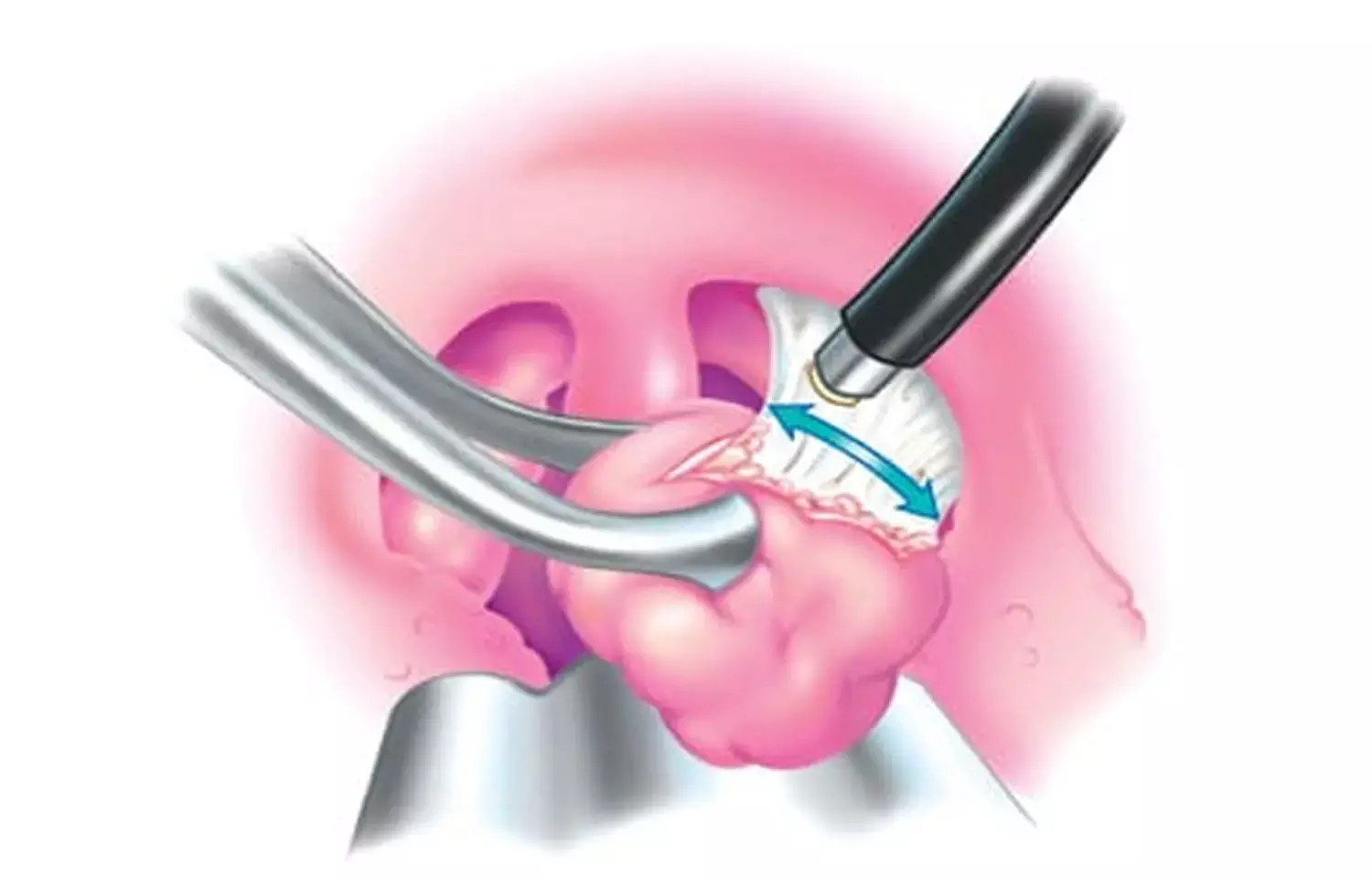
Turkey: Coblation crptolysis is a safe, effective, complication-less, minimally invasive, and practical alternative method for the treatment of halitosis (bad breath) due to tonsil caseums, a recent study in the American Journal of Otolaryngology has revealed.
Tonsil stones can cause halitosis and occur especially in crypts of palatine tonsils. Coblation cryptolysis is an alternative method for the treatment of tonsil caseum. The method includes passing a radiofrequency bipolar electrical current through a medium of normal saline which results in the production of a plasma field of sodium ions. In this study, Turgut Çelikb, Malatya Training and Research Hospital, Malatya, Turkey, and colleagues aimed to investigate the effectiveness of coblator cryptolysis treatment method in chronic caseous tonsillitis-induced halitosis.
The study included patients who underwent coblator cryptolysis surgery for halitosis due to chronic caseous tonsillitis. The efficacy of treatment and the presence of caseoma were evaluated with the Finkelstein test, organoleptic test and VAS before the procedure and at the 6th-month control after the treatment was completed.
Key findings of the study include:
- At the 6th month follow-up after the procedure (a single coblation cryptolysis) 23 of the patients (82.1%) were found to have no caseum.
- There was a statistically significant change in Finkelstein measurements before and after the procedure.
- Organoleptic measurements demonstrated that 21 patients had no halitosis postoperatively and the mean organoleptic test score was calculated as 0.39 ± 0.79 after the procedure.
- The recovery was statistically significant.
- The mean VAS score before coblation cryptolysis was 8.0 ± 1.33.
- 6 months after a single coblation cryptolysis session, the mean VAS score was 1.25 ± 1.78. This difference was statistically significant.
"Our results suggest that coblation crptolysis is an effective, safe, minimally invasive and practical alternative method in treatment of halitosis due to tonsil caseums," wrote the authors. "We did not observe any complication after the procedure."
Reference:
The study titled, "Coblation cryptolysis method in treatment of tonsil caseum-induced halitosis," is published in the American Journal of Otolaryngology.
DOI: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0196070921001769
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


