- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Morphological characteristics of vestibular aqueduct associated with occurrence of Meniere disease: Study
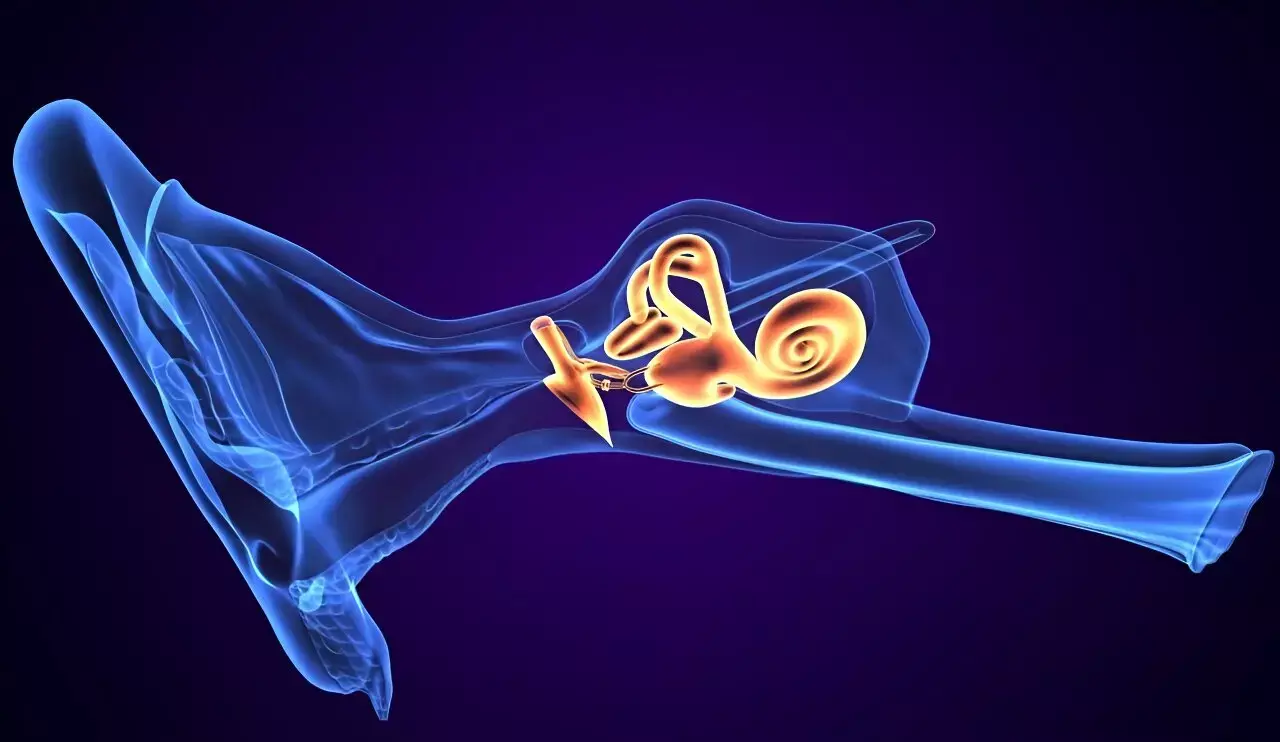
Morphological characteristics of vestibular aqueduct associated with the occurrence of Meniere disease suggest a study published in the Largnygoscope.
A study was done to investigate the relationship between vestibular aqueduct (VA) morphology and Meniere's disease (MD) using ultrahigh-resolution computed tomography (U-HRCT). Retrospective data were collected from 34 patients (40 ears) diagnosed with MD in our hospital who underwent temporal bone U-HRCT with the isotropic 0.05-mm resolution, magnetic resonance with gadolinium-enhanced, and pure-tone audiometry; 34 age- and sex-matched controls (68 ears) who underwent U-HRCT were also included. VA patency was qualitatively classified as locally not shown (grade 1), locally faintly shown (grade 2), or clearly shown throughout (grade 3). The width of the outer orifice and VA length and angle were quantitatively measured. Differences in VA morphology between the MD and control groups were analyzed.
The correlations between VA morphology and the degrees of hearing loss and endolymphatic hydrops (EH) were also analyzed. Results: VA was classified as grades 1–3 in 11, 17, and 12 ears in the MD group and 5, 26, and 37 ears in the control group, respectively. The patency differed significantly between the groups (p < 0.01). The width of the outer orifice and length of VA were significantly smaller in the MD group than those in the control group (p < 0.05). Both VA patency and length were correlated with the degree of EH in the cochlea and the vestibule (p < 0.05). No difference was found between VA morphology and the degree of hearing loss (p > 0.05). The morphological characteristics of VA were found to be associated with the occurrence of MD and the degree of EH.
Reference:
Huang, Y., Tang, R., Xu, N., Ding, H., Pu, W., Xie, J., Yang, Z., Liu, Y., Gong, S., Wang, Z. and Zhao, P. (2024), Association Between Vestibular Aqueduct Morphology and Meniere's Disease. The Laryngoscope. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.31339
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


